Figure 7. Knockdown of Hif1a in HCC abolishes miR-223 deficiency-driven angiogenesis and PD-1/PD-L1 activation.
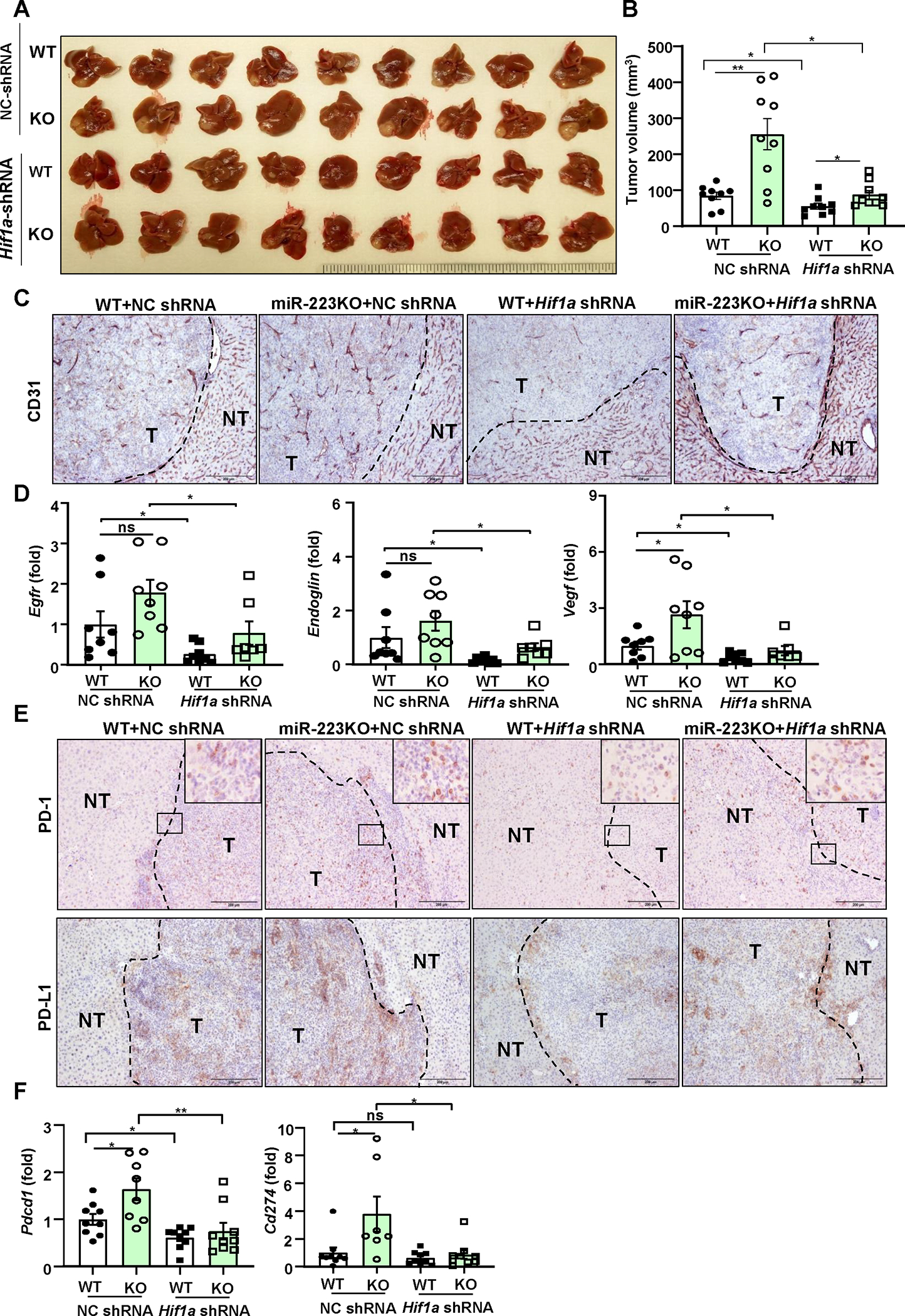
Four groups of mice were used: NC-shRNA or Hif1a-shRNA-transfected HCC in WT and miR-223KO mice in CCl4 plus Hepa1-6 orthotopic HCC model. NC-shRNA stands for negative control of Hif1a-shRNA. (A) Gross images of HCC tumor masses. (B) Tumor volumes were analyzed. (C) Representative images of CD31 staining in HCC sections (NT: non-tumor region; T: tumor region) of 4 groups are shown; scale bar=200 μm. (D) RT-qPCR analyses of angiogenesis-related genes in HCC tissues. (E) Representative images of PD-1/PD-L1 staining in HCC section of 4 groups are shown. The specific enlarged regions are shown on the right upper corner of the image. The numbers of PD-L1+ and PD-1+ cells were quantified and are shown in Supporting Figure 11E. (F) RT-qPCR analyses of Pdcd1 and Cd274 mRNA levels in adjacent non-tumor samples. values represent means ± SEM. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01.
