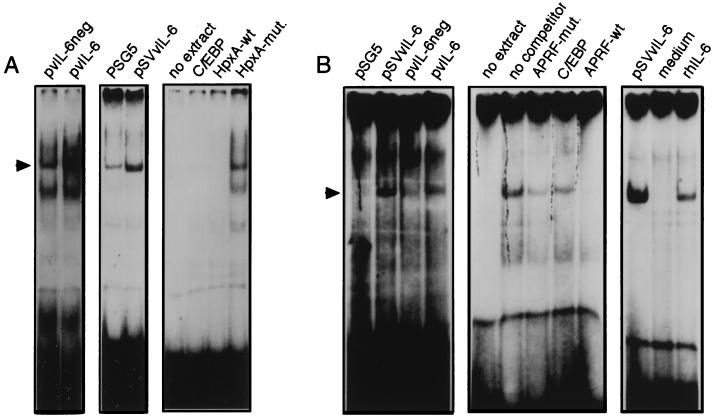
FIG. 2.
C/EBP- and STAT-related DNA binding activities induced by vIL-6. (A) Hep3B cells were transiently transfected with either pSVvIL-6, pvIL-6, pSG5, or pvIL-6neg, and growth media were harvested 48 h posttransfection. These were applied to fresh, serum-starved Hep3B cell cultures for 15 min before harvesting of cells for the preparation of nuclear protein extracts. Equal amounts of nuclear protein were used in EMSAs with the C/EBP-wt probe (see Materials and Methods). Induction of C/EBP binding activity was detected in the pvIL-6- and pSVvIL-6-transfected cells (left and middle panels, respectively [arrow]). Competition assays (right panel) were carried out with a 100-fold molar excess of unlabelled C/EBP-wt oligonucleotide, HpxA-wt (corresponding to sequences containing the C/EBP binding site in the −129 to −106 region of the hemopexin promoter [42]), and HpxA-mut. (containing base changes in the C/EBP core binding sequences). (B) Similar EMSAs were carried out for the detection of STAT binding activities with a probe (APRF-wt) derived from the α2-macroglobulin promoter (see Materials and Methods). vIL-6 induced complexes were evident (left panel), comigrated with complexes induce by rhIL-6 (500 U/ml) (right panel), and could be competed with a 100-fold molar excess of unlabelled APRF-wt but not with APRF-mut. (containing changes in the STAT binding site) or unrelated C/EBP-wt (C/EBP) oligonucleotides (middle panel).