Figure 2.
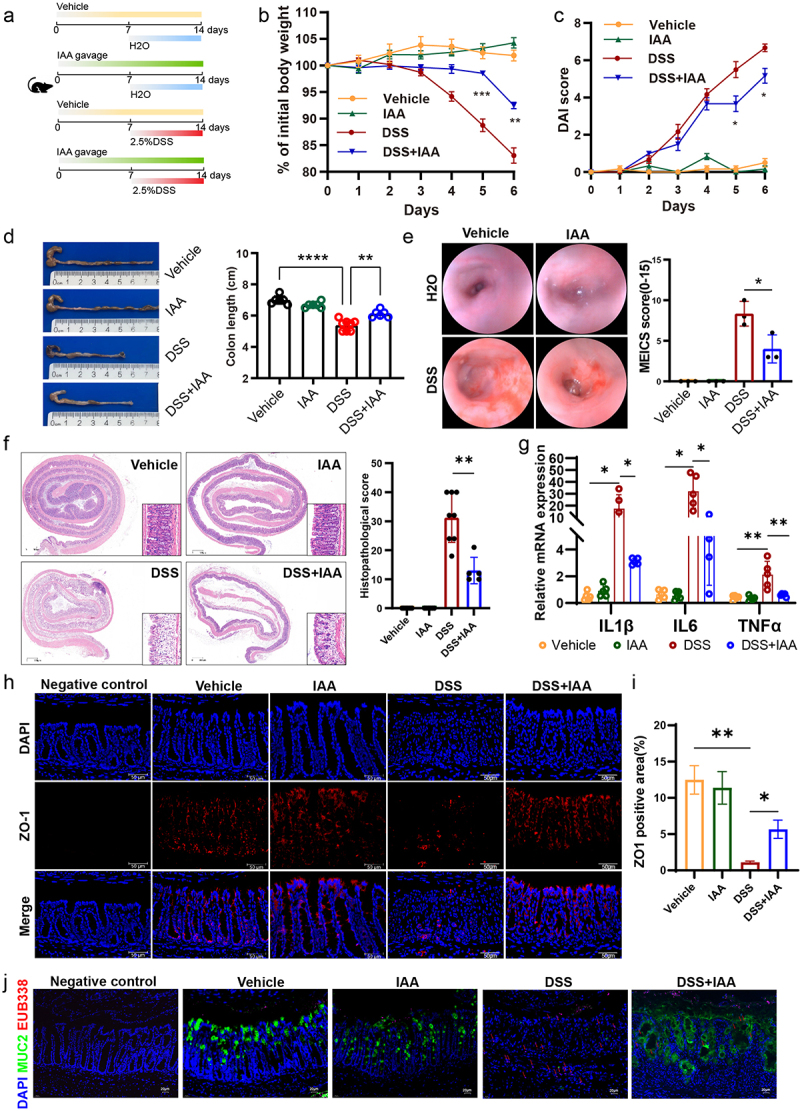
IAA ameliorated the severity of DSS-induced colitis and strengthened the gut barrier function.
(a) Animal treatment procedure. C57BL/6 mice (n=5-8) treated with or without IAA for 2 weeks and received H2O or 2.5% DSS in the last week. (b) Body weight changes. (c) Daily monitoring of DAI score including body weight loss, stool consistency, and fecal bleeding. (d) Representative images of the colon (left panel) and quantification of colon length (right panel). (e) Typical images of colonoscopy (left panel) and MEICS score (right panel). (f) Images of colon coil sections stained with H&E (left panel) and quantification of colon histopathological score (right panel) in DSS-induced colitis models. Scale bars: 300 µm. (g) The relative mRNA expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα. (h) Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 protein. Scale bars: 50 µm. (i) ZO-1 positive area statistics. (j) FISH using EUB338 probe for bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA (pink) as well as immunofluorescence of MUC2 (green) in colon tissue. Scale bars: 20 µm. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001.
