Figure 9.
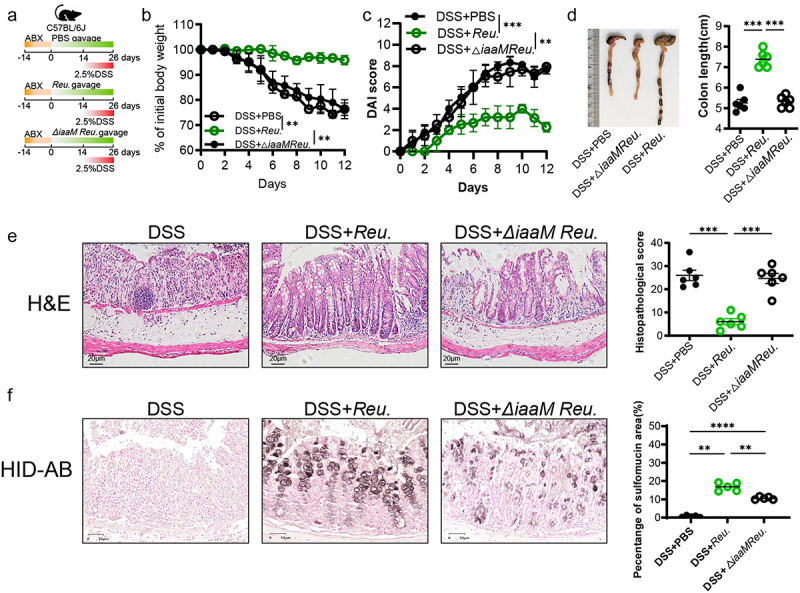
L. reuteri-derived IAA was required and sufficient to alleviate colitis and promote sulfation of mucin.
(a) Animal treatment procedure. C57BL/6 mice (n = 6) were administered an ABX for 2 weeks, then separately gavaged with PBS, Reu. and △iaaM Reu. for 26 d and received PBS or 2.5% DSS in the last 12 d. (b) Body weight changes. (c) Daily monitoring of DAI score. (d) Representative images of the colon (left panel) and quantification of colon length (right panel). (e) Histological images of H&E-stained colonic tissues (left panel) and colon histopathological score (right panel). Scale bars: 20 µm. (f) Representative micrographs (left panel) and quantifications (right panel) of HID-AB staining (sulfomucin stains brown) in colon sections. Scale bars: 50 µm. ns, not significant, *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001, ****p < .0001. ABX, antibiotic cocktail; △iaaM Reu., LactobacillusΔiaaM; Reu., L. reuteri;.
