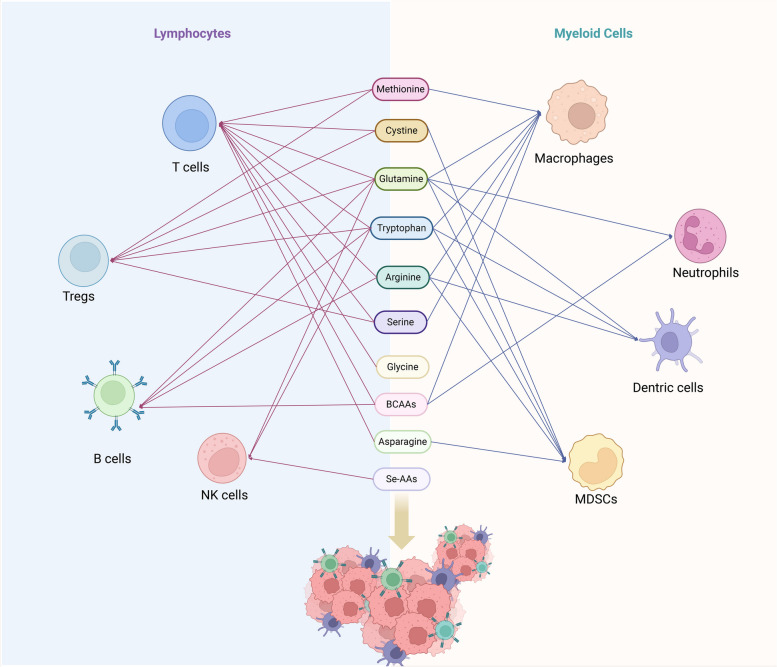
Fig. 3.
The influence of amino acids in regulating the activity and function of immune cells in microenvironment. Lymphoid immune cells encompass T cells, regulatory T cells, NK cells, and B cells, while myeloid immune cells consist of macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells, and MDSCs. Various studies have indicated that amino acids such as arginine, cysteine, glycine, glutamine, tryptophan, arginine, serine, BCAAs, aspartate, and selenium-containing amino acids play regulatory roles in the activation, proliferation, and function of immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. The red line represents the effect of amino acids on lymphocytes and the blue line represents the effect on myeloid cells. BCAAs branched-chain amino acids, MDSCs myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Image created with BioRender.com