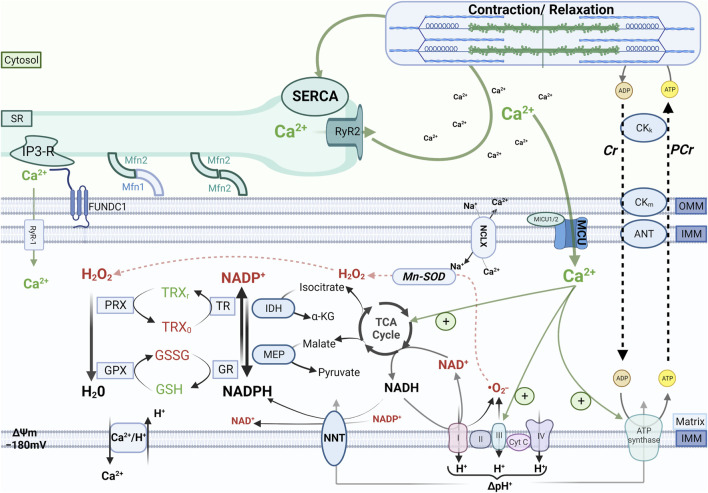
FIGURE 1.
Cardiac mechano-energetic coupling. In the healthy heart, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle produces the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). Electrons donated by NADH at complex I or by succinate at complex II of the respiratory chain are channeled through a series of electron acceptors that harness their energy to pump protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space. This process physiologically produces a certain amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) mainly due to incomplete reduction of oxygen to superoxide (.O2 −), which is rapidly converted to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by the manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD). In turn, H2O2 is reduced to H2O by peroxiredoxin (PRX) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX), which are regenerated in their active (reduced) form by a cascade of redox reactions fueled by NADPH. The main sources of mitochondrial NADPH are the TCA cycle enzymes isocitrate dehydrogenase and malate dehydrogenase and the nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT). When adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consumption increases, increased flux of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to mitochondria via the creatine kinase (CK) shuttle and Ca2+ accumulation in the mitochondrial matrix stimulate oxidative phosphorylation and the TCA cycle activity, respectively, thereby matching ATP supply and demand and providing reducing equivalents to maintain the redox state of mitochondrial antioxidant systems. Other abbreviations: SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum; RyR1 and RyR2, ryanodine receptors type 1 and type 2, respectively; MCU, mitochondrial calcium uniporter; NCLX, Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, IP3-R, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors; Mfn1 and Mfn2, mitofusin 1 and mitofusin 2, respectively; IMM and OMM, inner and outer mitochondrial membrane, respectively; FUNDC1, FUN14 domain containing 1; Cr, creatine; PCr, phosphocreatine; TRX, thioredoxin; GSH and GSSG, reduced and oxidized glutathione, respectively; GR, glutathione reductase; TR, thioredoxin reductase; IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase, MEP, malic enzyme; NNT, nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase; SERCA, SR Ca2+ ATPase.