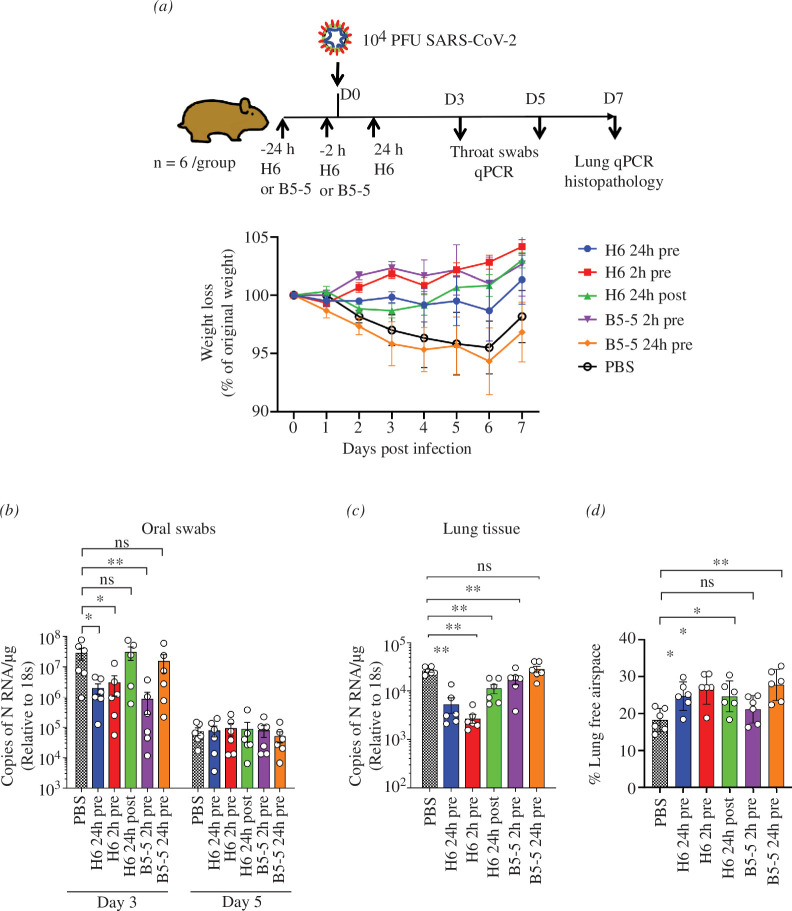
Figure 6.
Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of nanobody trimers (H6 and B5-5) in the Syrian hamster model of COVID-19. (a) Golden Syrian hamsters (n = 6 per group) were infected intranasally (IN) with SARS-CoV-2 strain Omicron BA.5 (105 pfu in 100 µl PBS). Individual cohorts were treated either 2 h pre-infection, 24 h pre-infection or 24 h post-infection (hpi) with 2 mg kg−1 100 μl of H6 or B5-5 IN as indicated or sham-infected with PBS. Animals were monitored for weight loss at indicated time points. Data represent the mean value ± s.e.m. (b,c) RNA extracted from oral swabs (b) and lung tissue (c) was analysed for SARS-CoV-2 viral load using qRT-PCR for the n gene levels by qRT-PCR. Assays were normalized relative to the levels of 18S RNA. Data for individual animals are shown with the median value represented by a horizontal line. Pairwise comparisons were made between groups using a Mann–Whitney U-test. **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.1. (d) Morphometric analysis. Haematoxylin–eosin (HE)-stained sections were scanned and analysed using the software program Visiopharm to quantify the area of non-aerated parenchyma and aerated parenchyma in relation to the total area. Results are expressed as the mean-free airspace in lung sections. Pairwise comparisons were made between groups using a Mann–Whitney U-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.