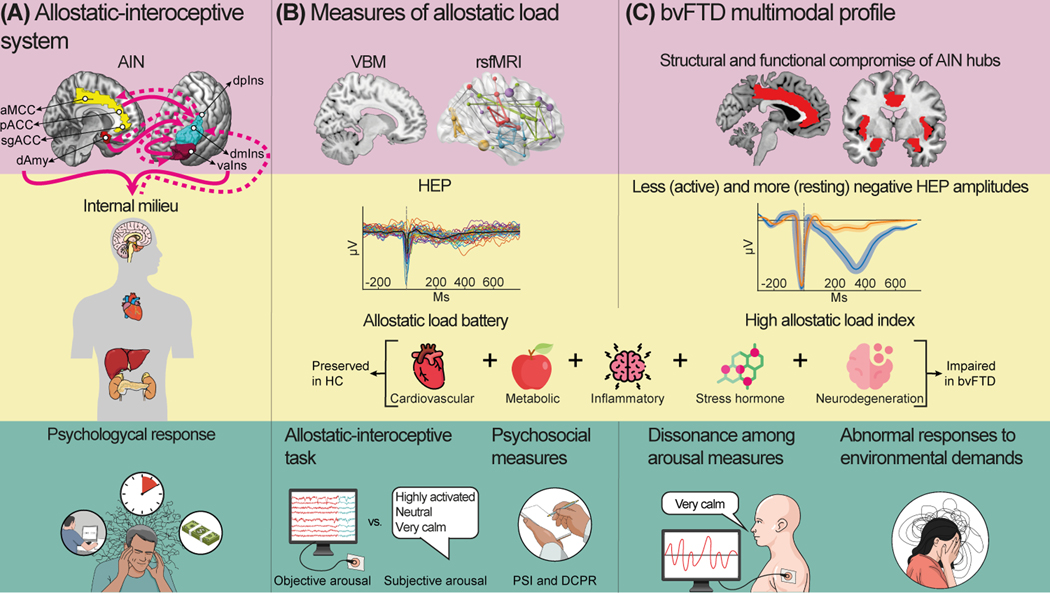
Figure 2.
Levels of the allostatic–interoceptive system and its potential characterization in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD). Multimodal allostatic load measurement can be used at different levels to characterize bvFTD symptomatology and physiopathology. The allostatic–interoceptive system (A) relies on the allostatic– interoceptive network (AIN), whose main hubs include the anterior mid-cingulate cortex (aMCC), pregenual anterior cingulate cortex (pACC), subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (sgACC), dorsal amygdala (dAmy), agranular insula (vaIns), dorsal mid-insula (dmIns), and dorsal posterior insula (dpIns). Specifically, the limbic cortices send prediction signals (unbroken magenta lines) and receive prediction error signals (dashed magenta lines) from the internal milieu, evoking psychological responses. Accordingly, multimodal measures of allostatic load can be used (B). At the cerebral level, the structure of the AIN hubs can be assessed by voxelbased morphometry (VBM) technique and its functional connectivity by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rsfMRI) technique. The cardiocerebral level can be evaluated by heartbeat-evoked potential (HEP). Moreover, the peripheral level can be assessed by cardiovascular, metabolic, inflammatory, stress hormone, and neurodegenerative biomarkers, constituting an allostatic load battery. Finally, the psychological level can be evaluated by the allostatic–interoceptive task and psychosocial measures such as the psychosocial index (PSI) and the diagnostic criteria for psychosomatic research (DCPR). Some multimodal impairments are expected in bvFTD patients (C). At the cerebral level, the AIN is selectively compromised in bvFTD, along with early structural and functional compromise of core AIN hubs. At the cardiocerebral level, less negative HEP during active tasks and more negative resting-state HEP (rsHEP) in resting state and noncardiac monitoring tasks are also expected. At the peripheral level, bvFTD may present altered biomarker parameters, leading to a high allostatic load index compared with healthy controls (HC). At the psychological level, bvFTD patients will present a dissonance among the objective and subjective arousal measures and abnormal responses to environmental demands. Figures in panels (B) and (C) are illustrational examples and do not represent actual data.