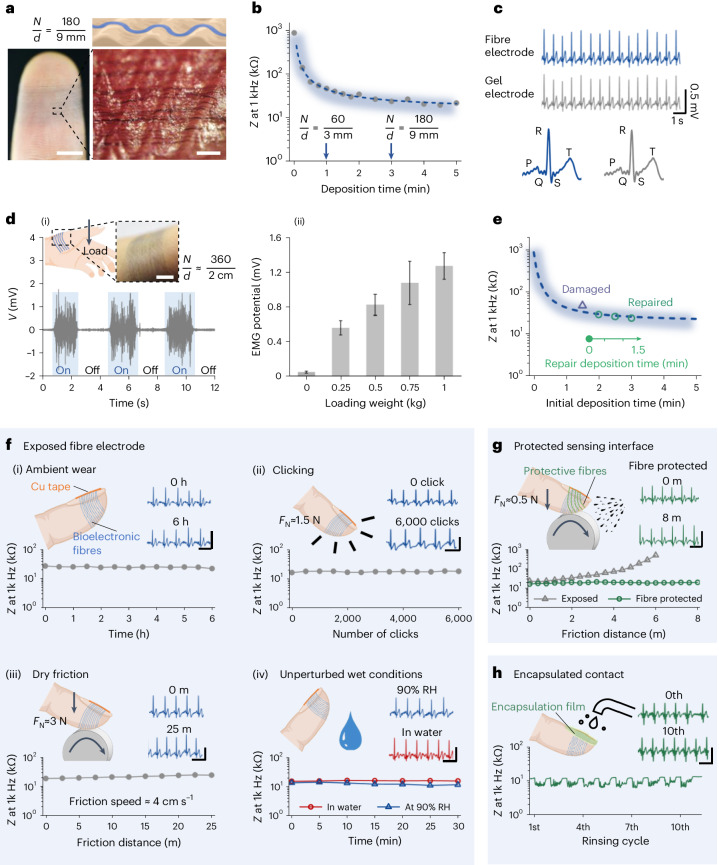
Fig. 3. Tailored imperceptible on-skin electrodes.
a, An illustration (top) showing fibres covering the ridges of the fingerprints, where indicates the number of fibres N across a distance d; and the experimental evidence is provided by the photographs (bottom row) showing the complete fibre array on a fingertip and the zoom-in view of the fibres follow the ridges of the fingerprints (scale bars left to right, 5 mm, 500 μm). b, Contact impedance versus deposition time on the fingertip. c, Comparison of ECG signals acquired by fibre and gel electrodes at the same time (signal correlation P = 0.99). d, (i) An array of fibres deposited on the thumb muscle region, where ON/OFF loading on the thumb results in clear on/off EMG signals detected by the fibres (scale bar, 1 cm). (ii) Bar chart to depict variations in absolute EMG amplitude from the thumb muscle region against different loading weights on the thumb (data are presented as mean absolute EMG values ± standard deviation of EMG measured for around 5 s in each case). e, Facile repairability of the exposed fibre arrays. The triangular symbol indicates the impedance of the fibre arrays after being deliberately damaged by abrasion, and then new fibres are deposited on demand to repair as indicated by the circular symbols. f, The stability of exposed fibre electrode (exposed bioelectronic fibres on skin) under the conditions of (i) ambient wearing; (ii) mouse clicking; (iii) dry friction wear with a plastic surface (at a surface speed of 4 cm s−1 under around 40% relative humidity (RH) environments); (iv) simulated ‘wet’ conditions without mechanical disturbance. g, Wet friction (at a surface speed of around 4 cm s−1) of exposed and cellulose-based fibre protected sensing interface. h, Rinsing under running water (the sensing interface is protected with cellulose-based fibres and the fibre contact is encapsulated with a cellulose-based film) (ECG scales for f,g, horizontal time scale 1 s, vertical voltage scale 0.5 mV). (a–e, typical results from n = 5 volunteers, f–h, typical results from n = 3 volunteers, for all experiments with n > 3 independent experiments performed on each volunteer).