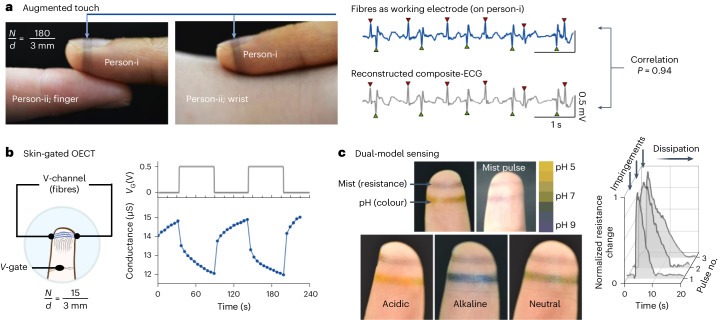
Fig. 4. Imperceptible augmentation.
a, Augmented touch perception via dual-ECG sensing with person-i wearing bioelectronic fibre arrays and person-ii without. The dual-ECG signal acquired through the fibre array is compared with the reconstructed composite-ECG signal from validation gel electrodes. The red downward facing and green upward facing triangles indicate the R peaks of person-i and person-ii, respectively. b, A breathable skin-gated OECT on a fingertip; the OECT displays a response time in the 60 s range. c, Dual-modal sensing for augmented perception of mist pulses with acidic, alkaline and neutral compositions distinguished through colorimetric and electrical readouts. The mist pulse photographs show an example of a neutral mist pulse, and the fibre resistance change was recorded by applying three consecutive neutral mist pulses (normalized resistance change is calculated as , where R* is the peak resistance and R0 is the initial resistance; the initial resistances of the fibre arrays are in the range of 10 kΩ). a–c, Typical results from n = 5 volunteers, with n > 3 independent experiments performed on each volunteer.