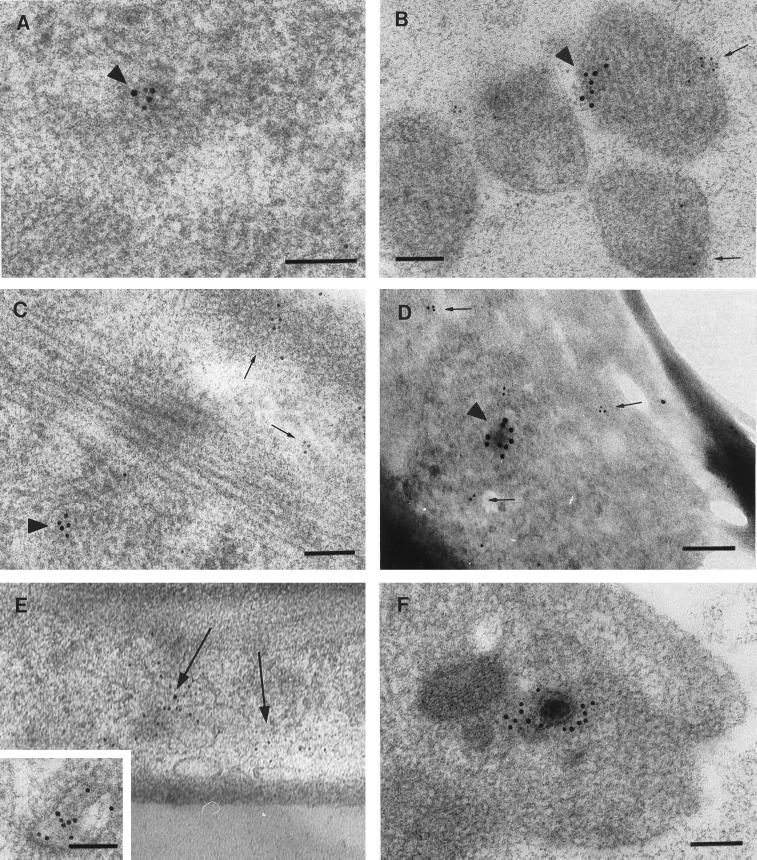
FIG. 7.
TIEM of axons in the outside chamber of the model fixed 24 h after HSV infection of the inner chamber. Bars, 100 nm. (A) Colocalization of gold particles labelling VP5 (10 nm) and VP16 (5 nm) in a cluster. (B and C) Spatial separation of collections of immunolabel for VP5 (10 nm; arrowheads) and glycoprotein C (5 nm; arrows) in a cross section (B) and longitudinal section (C) of axons. (D) Similar pattern to panels B and C with double labelling for VP5 (10 nm) and glycoprotein B (5 nm); the immunolabel for VP5 was arranged around a dense structure, and that for gB was arranged around microvesicles. Identical findings were obtained with immunolabelling for gD. (E) Immunolabel for gB 5-nm gold particles was arrayed around the walls of 60- to 200-mm-diameter vesicles. The inset shows a higher-magnification view of glycoprotein immunolabelling of an axonal vesicle. Bar, 100 nm. (F) Distinct example of a nucleocapsid with immunolabel (10 nm) for VP16. Although this section was also immunolabelled for glycoprotein, none is present near this capsid. Ultrathin sections immediately before and after this section showed only indistinct virus structures.