Figure 6.
TRB4 and TRB5 are required for leaf curling and early flowering in clf-29 mutant plants
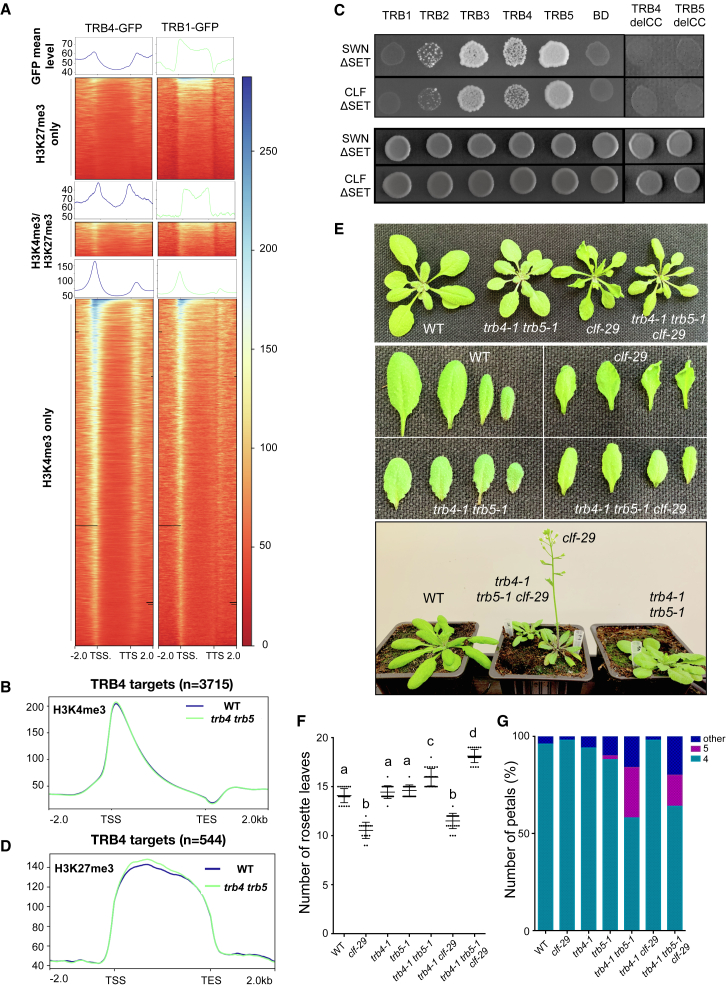
(A) Metagene plots and heatmaps showing ChIP-seq signals of TRB4-GFP or TRB1-GFP over genes enriched in H3K27me3, H3K4me3, or both histone marks as determined by ChIP-seq analysis.
(B) Metagene plot showing enrichment of H3K4me3 over TRB4-target genes.
(C) Interaction of Arabidopsis TRB1–5, TRB4delCC, and TRB5delCC (lacking the coiled-coil domain) proteins (as bait) with CURLY LEAF (CLF) and SWINGER (SWN) proteins (lacking the SET domain) (as prey) probed in the Y2H system. Upper panel: yeast strains growing on synthetic medium lacking Leu, Trp, and His reveal interactions. Lower panel: growth of zygotes on synthetic medium lacking Leu and Trp, selecting for the presence of the bait and prey vectors for interactions.
(D) Metagene plot showing enrichment of H3K27me3 over TRB4-target genes.
(E) Representative WT, trb4-1 trb5-1, clf-29, and trb4-1 trb5-1 clf-29 triple-mutant plants at 3 weeks (top, middle) and 4 weeks (bottom) after sowing. Loss of TRB4 and TRB5 in the clf-29 mutant background abolishes the curly leaf and early-flowering phenotypes.
(F) Mean number of rosette leaves at bolting in the indicated genotypes.
(G) Mean number of petals observed in flowers from the indicated genotypes.