Figure 7.
TRB4 and TRB5 function as transcriptional activators of FT and SOC1 flowering regulators
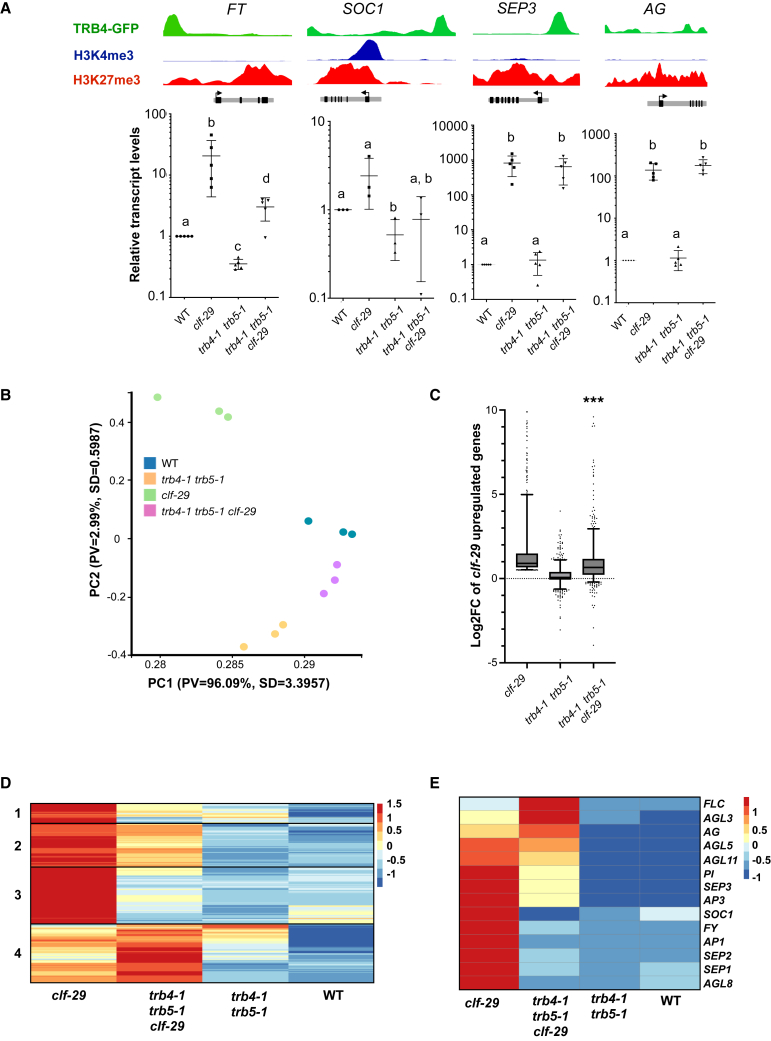
(A) Top: Genome Browser views showing binding of TRB4 and enrichment in H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 at FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CO 1 (SOC1), SEPALLATA3 (SEP3), and AGAMOUS (AG) as determined by ChIP-seq in 7-day-old seedlings. Bottom: relative transcript levels of FT, SOC1, SEP3, and AG in rosette leaves from WT, trb4-1 trb5-1, clf-29, and trb4-1 trb5-1 clf-29 triple-mutant plants at 3 weeks of age as determined by RT–qPCR. Different letters indicate significant differences among samples by the Mann–Whitney test (p < 0.01).
(B) Principal component analysis of transcriptomes generated from 3-week-old rosette leaves of WT, trb4-1 trb5-1, clf-29, and trb4-1 trb5-1 clf-29 triple-mutant plants.
(C) Boxplot presenting log2FC relative to WT for genes upregulated in clf mutants and enriched in H3K27me3 (n = 762) in trb4-1 trb5-1, clf-29, and trb4-1 trb5-1 clf-29 triple-mutant plants (∗∗∗p < 0.0001, Mann–Whitney test between clf29 and trb4-1 trb4-1 clf29 mutants).
(D)Z-score hierarchical clustering heatmap of the same genes as in (C).
(E)Z-score hierarchical clustering heatmap of the MADS-box genes upregulated in the clf29 mutant.