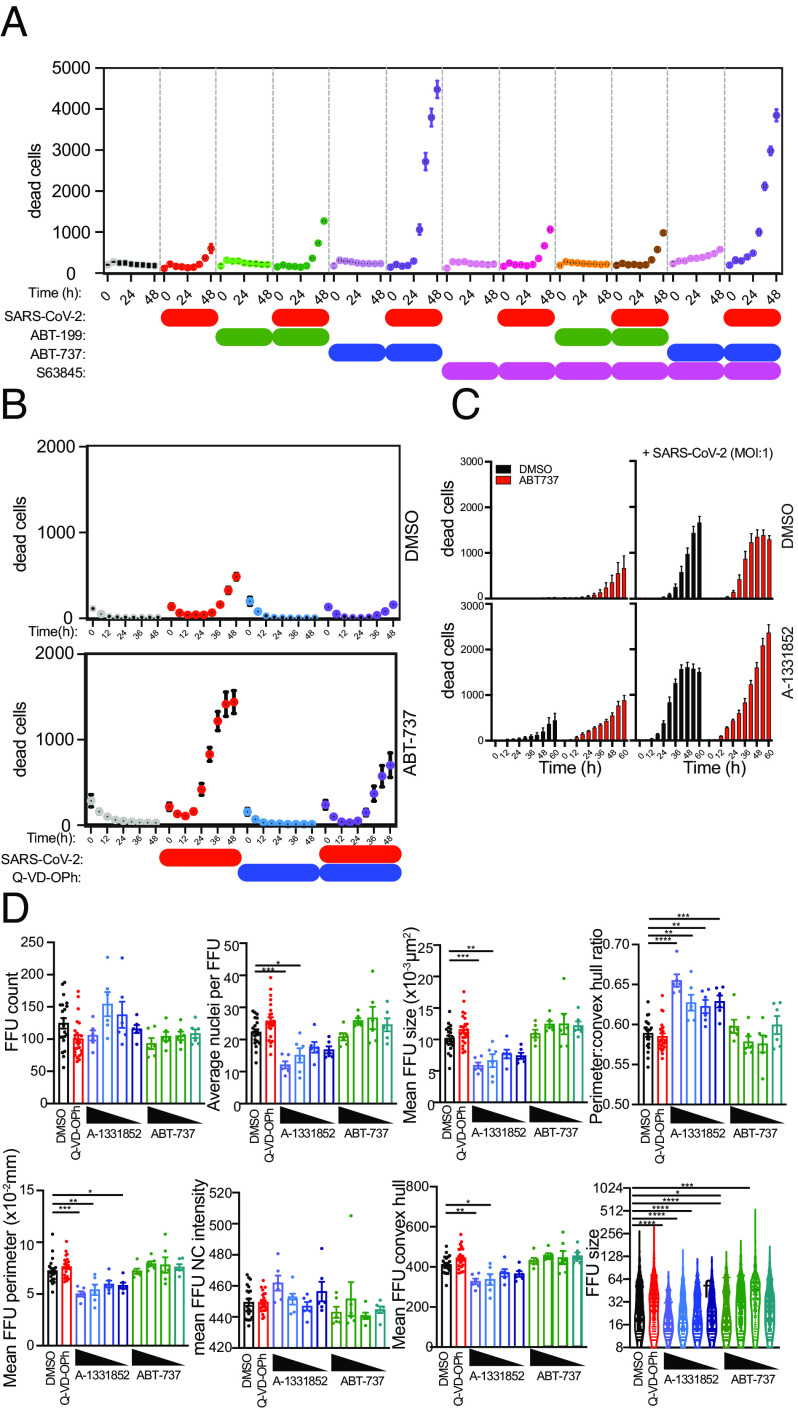
Fig. 5.
Human lung cell viability in LOs following SARS-CoV-2 infection is reduced by BH3 mimetics but increased by caspase antagonists. See SI Appendix, Fig. S8 for live cell phase contrast imaging of LOs showing morphological changes triggered by viral vs. mock infection (showing daily progressive dissolution of integrity of the LOs. The FFU assay is also illustrated there. (A–D) SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung cells reduces their viability. Cell death was tracked using PI uptake. Cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 and then treated with ABT-737 (an inhibitor of prosurvival Bcl-2 family proteins Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Bcl-w), ABT-199 (which modestly activates proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins), S63845 (an antagonist of Mcl-1), or Q-VD-OPh (a caspase inhibitor). Viability was monitored every 6 h. Data from three independent experiments are shown. (B) Q-VD-OPh blocked virus-induced death, consistent with a role for apoptotic caspases. (C and D) ABT-7 and ABT-199 accelerated cell death (the former more than the latter), consistent with a role for Bcl-2 family proteins in regulating the dynamics of cell viability during infection.