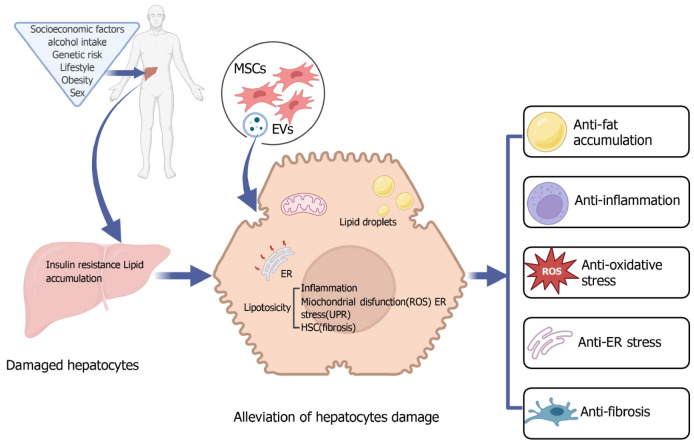
Figure 1.
The therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells and mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived secretory factors in managing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatic insulin resistance and lipid accumulation are exacerbated by multiple detrimental factors, resulting in hepatocyte damage. The transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and their derived secretory factors introduces a holistic approach to liver health. These cells not only regulate lipid metabolism and enhance insulin sensitivity but also reduce fat accumulation in the liver. Their anti-inflammatory properties are emphasized by their ability to inhibit the activation of immune cells, such as Kupffer cells and natural killer cells, and by their role in reducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, MSCs produce antioxidants that neutralize reactive oxygen species in the liver, thereby mitigating both oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. In countering liver fibrosis, MSCs play a prominent role by suppressing hepatic stellate cells, releasing anti-fibrotic factors, and aiding in hepatocytes repair. Moreover, these stem cells secrete cytokines that are crucial for liver tissue repair and regeneration. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; EVs: Extracellular vesicles; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell.