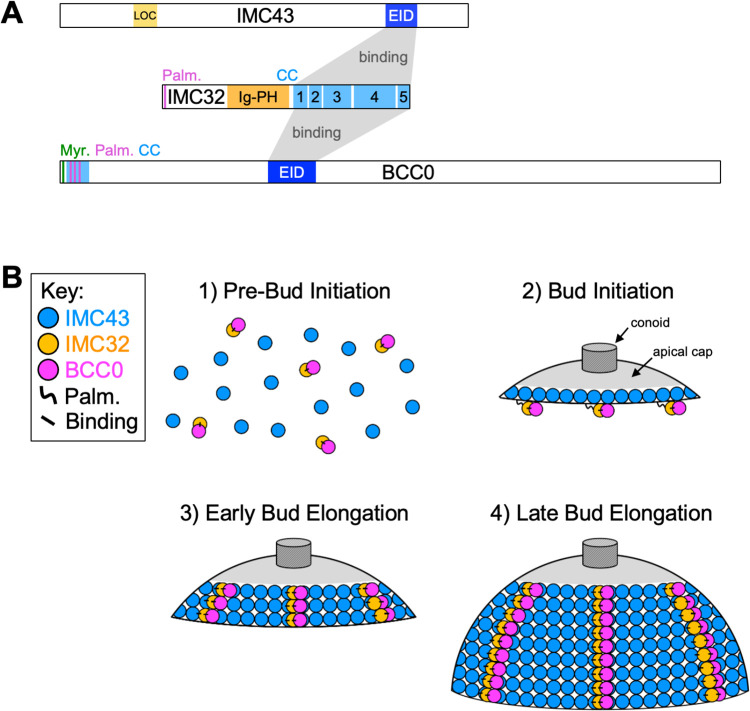
Fig 8. Summary.
A) Diagram depicting interactions between the components of the essential IMC43-IMC32-BCC0 daughter bud assembly complex. Grey boxes indicate binding interactions between the essential interaction domains (EID) of IMC43 and BCC0 with IMC32’s C-terminal coiled-coil domains. “Myr.” = predicted myristoylation site. “Palm.” = predicted palmitoylation site. “CC” = coiled-coil domain. B) Diagram summarizing the current model for how IMC43, IMC32, and BCC0 assemble onto the developing daughter cell scaffold during endodyogeny. Just before bud initiation (step 1) expression of IMC43, IMC32, and BCC0 increases. IMC32 and BCC0 bind to each other at this point. During bud initiation (step 2) IMC43 recruits to the early daughter cell scaffold independently. IMC32 is recruited to the membranes of the early daughter cell scaffold via palmitoylation. BCC0 remains bound to IMC32. During early bud elongation (step 3), IMC32 binds to IMC43, securely locking it into the daughter cell scaffold. BCC0 remains bound to IMC32. Short stripes of IMC32 and BCC0 can be seen at this point, which become more prominent as bud elongation continues (step 4).