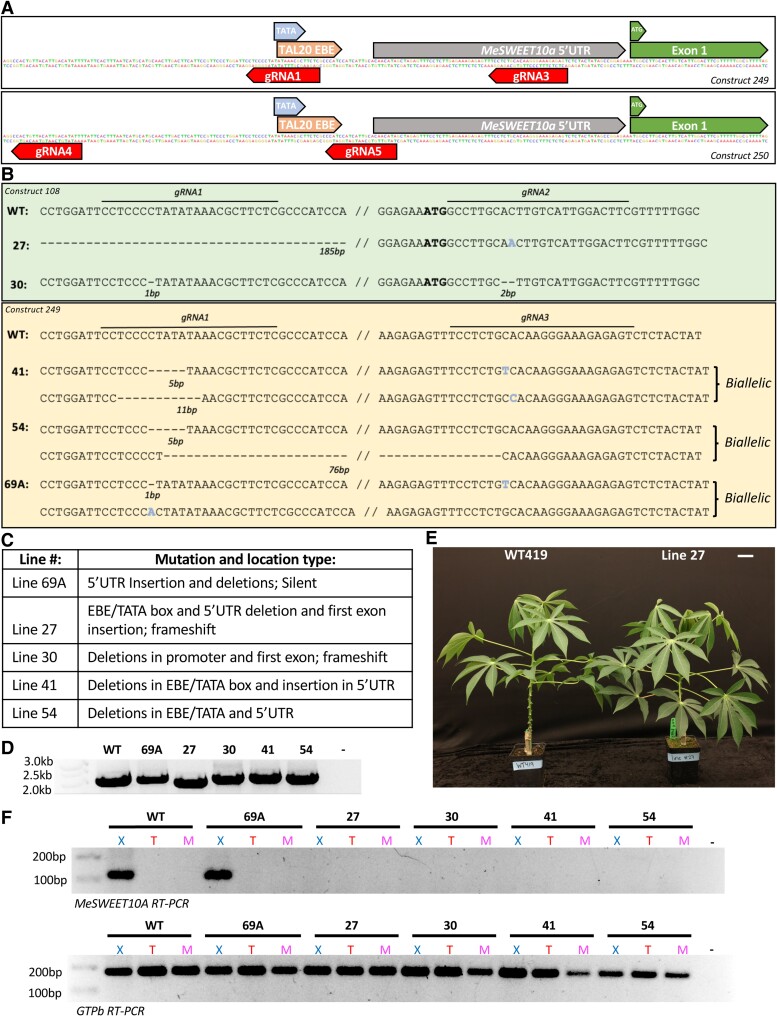
Figure 2.
Additional MeSWEET10a mutant lines lack TAL20-mediated induction. A) Graphic depicting the MeSWEET10a region of interest, TAL20 EBE site, TATA box, translation start site (ATG), and gRNA target sites for constructs 249 and 250. B) Genotyping of MeSWEET10a mutant lines recovered from constructs 108 and 249 based on Sanger sequencing. Text indicates sequences at the region of interest for wild-type plants and mutant lines #27, 30, 41, 54, and 69A. The location of each gRNA target site and the corresponding gRNA number are noted. Deletions are indicated by “-” and the number of deleted base pairs (bp) is indicated below each deletion. Insertion or base substitution events are noted. The “biallelic” text to the right of the sequence distinguishes lines that are heterozygous for mutant alleles. C) Table with description of mutation and location type for each mutant line. D) PCR products generated by primers targeting the MeSWEET10a region in gDNA from WT and edited lines. E) Representative image of wild-type cassava (left) and line 27 (right) plants grown from stake cuttings in greenhouse. Scale bar = 14 cm. F) RT-PCR of wild-type cassava and MeSWEET10a mutant lines infected with Xpm, Xpm△TAL20, and mock treatments. The top gel shows results of RT-PCR with primers amplifying MeSWEET10a with an expected product size of 123 bp. The bottom gel shows results of RT-PCR with primers amplifying the housekeeping gene GTPB as a control for sample loading with an expected product size of 184 bp. “-” denotes a negative water control. X, Xpm; T, Xpm△TAL20; M, mock.