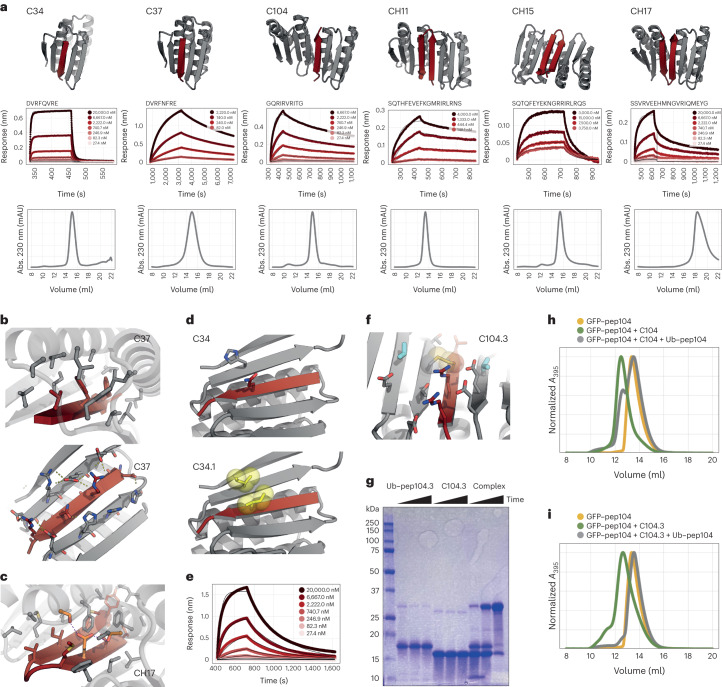
Fig. 2. Characterization of designed peptide binders.
a, Design models for peptide binders (binder, gray; peptide, dark red). BLI traces with kinetic fits and SEC (S75 Increase 10/300) chromatograms of the purified binders are shown below the corresponding models. mAU, milli absorbance units. b, Detailed views of the solvent-exposed interface (bottom) and the buried interface (top) of C37. C-α atoms as spheres. c, Detailed view of the buried part of the interface of hairpin binder CH17 with the designed hydrogen-bond network depicted in orange sticks. d, Models of parent design C34 (top) and C34.1 (bottom) where a hydrophobic interaction pair (yellow sticks/spheres) is introduced to improve affinity. e, BLI traces of C34.1 binding to its peptide immobilized on biosensors. f, View of the designed interface disulfide on C104.3 (disulfide in spheres and sticks; additional redesigned residues in cyan). g, Representative nonreducing SDS−PAGE gel showing disulfide formation (time points of 0 min, 90 min and overnight). The experiment was reproduced twice with two independent protein preparations. Ub, ubiquitin. h, SEC traces of preformed noncovalent C104 complex + GFP−pep104. i, SEC traces of preformed covalent disulfide-linked C104.3 complex + GFP−pep104.