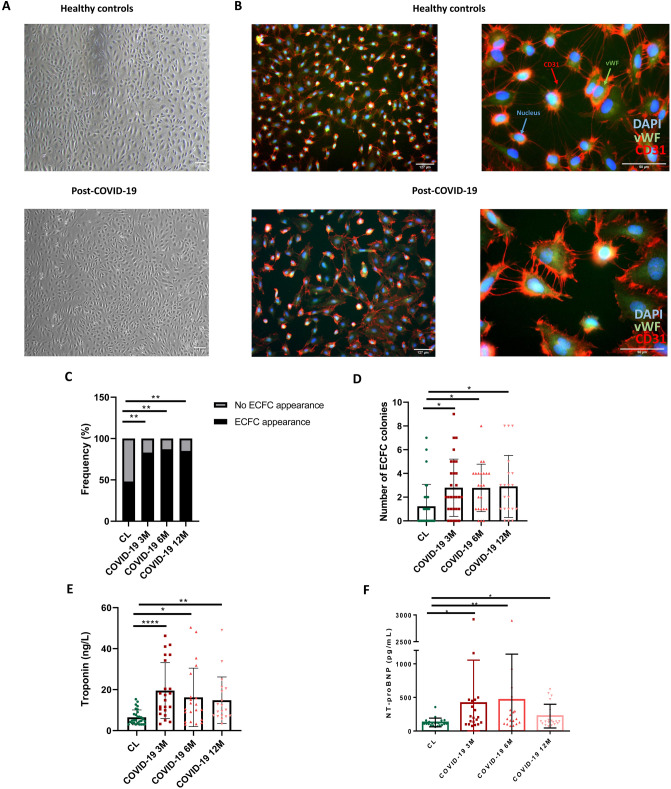
Fig. 1.
A ECFC colonies of CL and post-COVID-19 patients resembling typical cobblestone morphology appeared within 1–3 weeks of culture (4x). B Immunofluorescence staining for CD31 (red), vWF (Green), nuclei (blue) of endothelial cells from healthy controls and post-COVID-19 patients (10 ×) (60x). Blue arrows represent the nucleus, green arrows represent vWF and red arrows represent CD31. C. Frequency of appearance and no appearance of ECFC colonies in healthy controls and 3, 6 and 12-months post-COVID-19 patients, Chi-square test, **P < 0.01. D Number of ECFC colonies in healthy controls and 3, 6 and 12-months post-COVID-19 patients, Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, *P < 0.05. E Levels of troponin (ng/L) in healthy controls and 3, 6 and 12-months post-COVID-19 patients, Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.001. F NT-proBNP (pg/mL) in healthy controls and 3, 6 and 12-months post-COVID-19 patients, Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. DAPI 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, vWF Von Willebrand factor, CD31 cluster of differentiation 31, CL healthy control, ECFC endothelial colony-forming cells, NT-proBNP N-terminal-pro hormone B-type natriuretic peptide