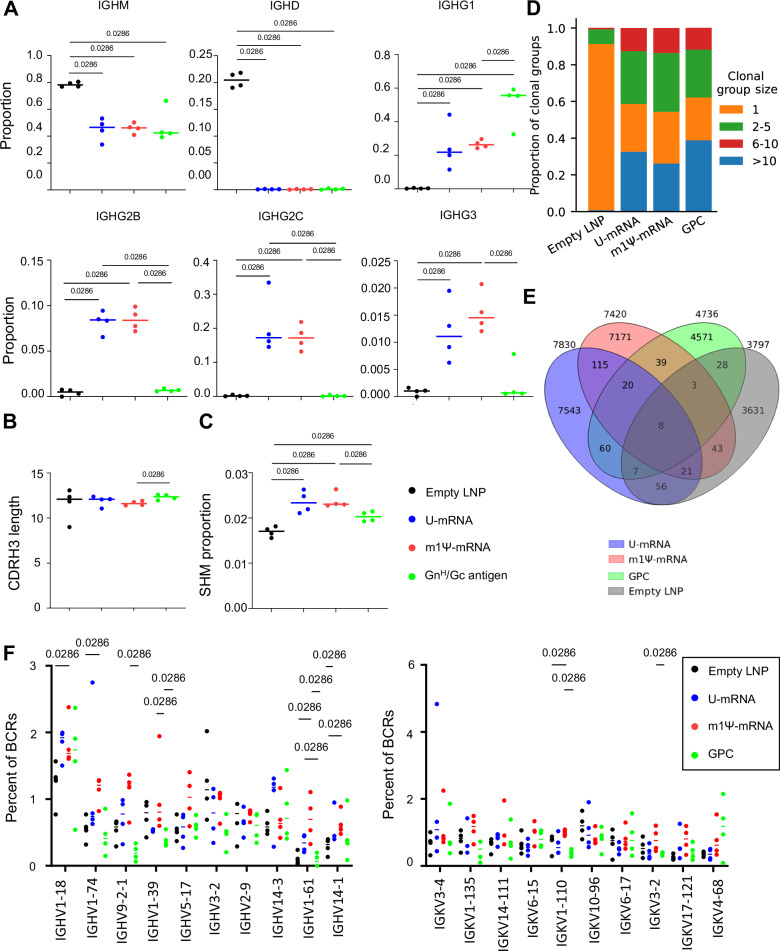
Fig. 4. ANDV U-mRNA and m1Ψ-mRNA vaccines induce comparable class-switching and somatic hypermutation in mouse B cells.
B cells from the mouse study presented in Fig. 3 were subjected to single-cell BCR RNA sequencing (n = 4 animals/group). A Proportions of cells expressing the C region of the heavy chain of various immunoglobulins. B Average lengths of antibody heavy chains CDR3 regions (number of amino acids). C Average proportion of somatic hypermutation in CDRH3. D BCRs were clustered based on Levenshtein distance and matching heavy V genes. Size bins represent a number of BCRs in each clonal family, ranging from unique BCRs to highly expanded clonal groups (>10). E Number of overlapping clones between U-mRNA and m1Ψ-mRNA vaccine groups. Little overlap between the groups was observed, but U-mRNA and m1Ψ-mRNA vaccine groups showed the most with seven public clonal groups. F U-mRNA and m1Ψ-mRNA vaccine groups show different V gene usage for heavy (left) and light (right) chains. U-mRNA and m1Ψ-mRNA vaccine groups both used IGHV1-18 and IGHV-74 with the highest frequency, but there were differences at lower ranks. Median values, two-tailed unpaired Mann–Whitney test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.