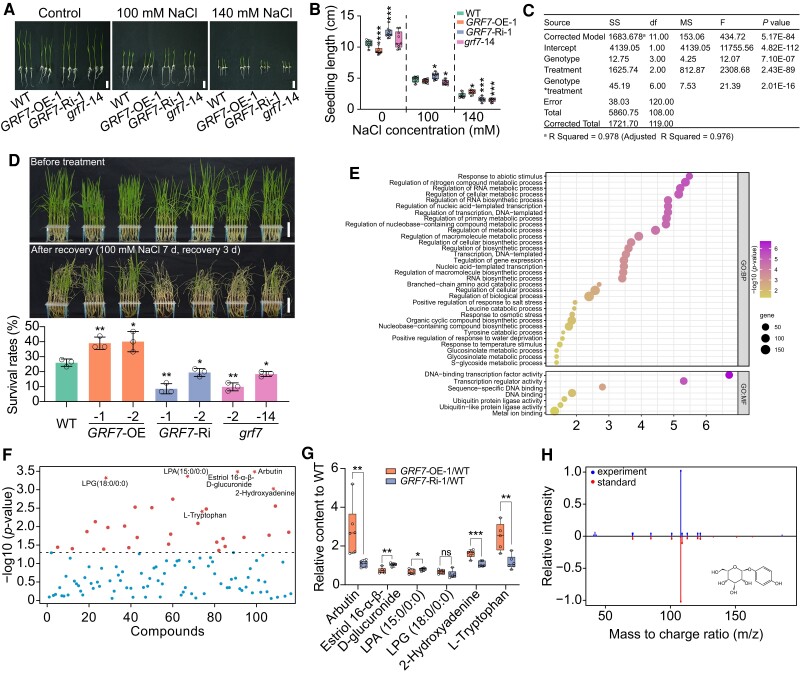
Figure 1.
Overexpression of OsGRF7 enhances tolerance to salinity stress with the involvement of arbutin. A) Phenotypes of WT and OsGRF7 transgenic seedlings treated with different concentrations of NaCl. Bars = 2 cm. B) Effects of different concentrations of NaCl on seedling length B) in the WT and OsGRF7 transgenic lines. Values are means ± SDs (n = 10 independent seedlings). C) Two-way analysis of variance of the contribution of genotype, treatment, and their interaction to seedling length. SS, type III sum of squares. df, degree of freedom. MS, mean square. F, freedom. D) Fifteen-day-old seedlings of WT and OsGRF7 transgenic lines were treated with 100 mM NaCl for 7 d and recovered for 3 d. Bars = 5 cm. Values are means ± SDs of 3 biological replicates. E) Gene ontology enrichment analyses of downregulated genes in grf7-14 after salt treatment. F) One-way analysis of variance of all identified metabolites in the WT and OsGRF7 transgenic lines. The six selected metabolites for further analysis are marked with red pentagrams. G) Relative levels of the six selected metabolites in F). H) Comparison of MS/MS spectra between experimental samples and the arbutin standard. Values are means ± SDs of 3 biological replicates. For B) and G), the line in the middle of each box represents the 50th percentile. The bottom and top lines represent the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively. The whiskers are the minimum and maximum values. WT, wild type. GRF7-OE, OsGRF7 overexpression lines. GRF7-Ri, OsGRF7 RNAi lines. grf7, OsGRF7 knockout lines. ns, no significant difference. For this figure, asterisks indicate significant differences between the wild type and the other genotypes by a two-tailed Student's t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001).