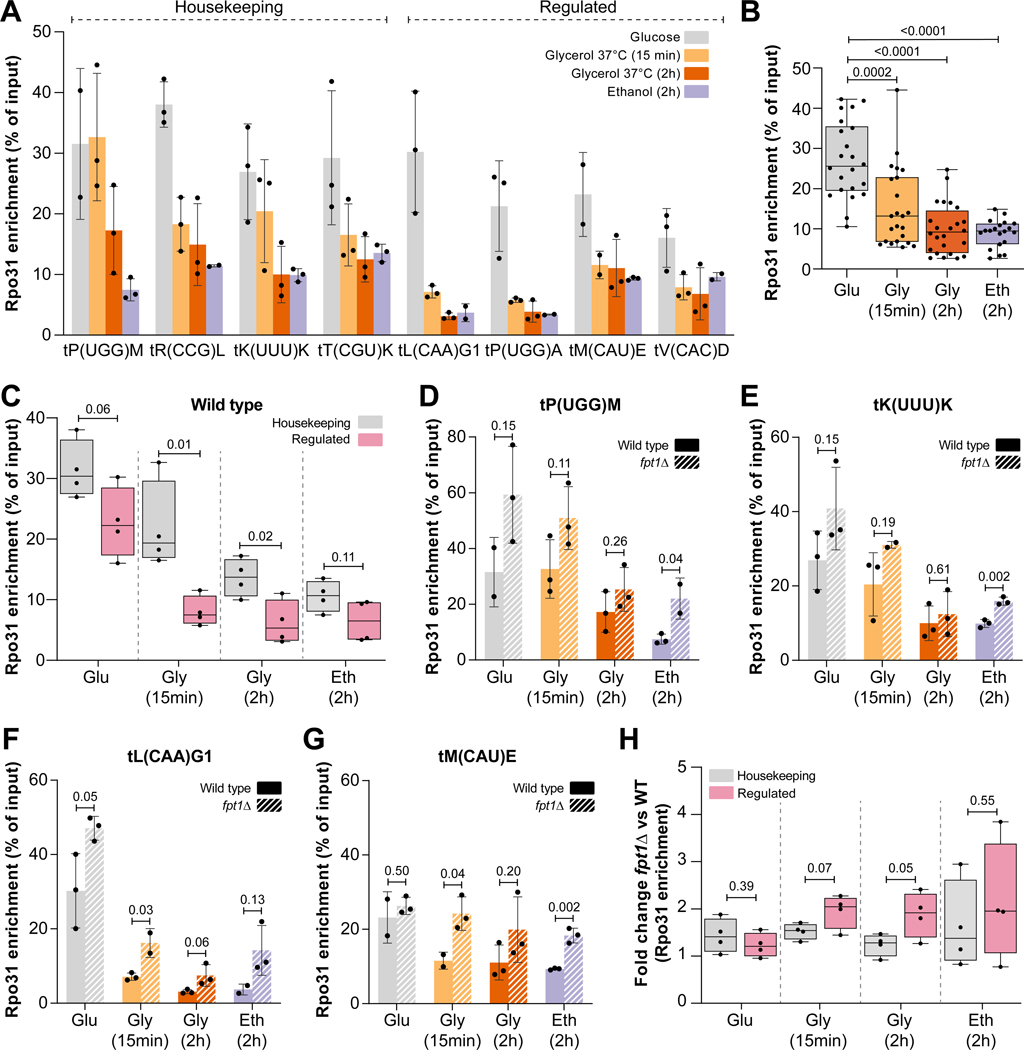
Figure 4. Deletion of Fpt1 compromises eviction of RNAPIII upon nutrient perturbation.
(A) Rpo31 enrichment (TAP-ChIP) in glucose, glycerol 2h or 15 min (37°C) and ethanol 2h (n = 3 ± SD). (B) Stacked Rpo31 enrichment from (A). Statistics: Welch-corrected unpaired two-tailed t-test. (C) Rpo31 enrichment (TAP-ChIP) in WT at housekeeping tRNA genes (grey, n = 4) and regulated tRNA genes (pink, n = 4) in glucose, glycerol 2h and 15 min (37°C), and ethanol 2h. For each tRNA gene, the average of three biological replicates is shown. Whiskers indicate the minimum and maximum. Statistics: unpaired two-tailed t-test. (D-G) Rpo31 enrichment (TAP-ChIP) in WT and fpt1Δ (n = 3 ± SD) in glucose, glycerol 2h and 15 min (37°C), and ethanol 2h. Statistics: unpaired two-tailed t-test. (H) Fold change between WT and fpt1Δ for Rpo31 enrichment at housekeeping tRNA genes (grey, n = 4) and regulated tRNA genes (pink, n = 4). For each tRNA gene, the average of three biological replicates is shown. Whiskers indicate the minimum and maximum. Statistics: unpaired two-tailed t-test.