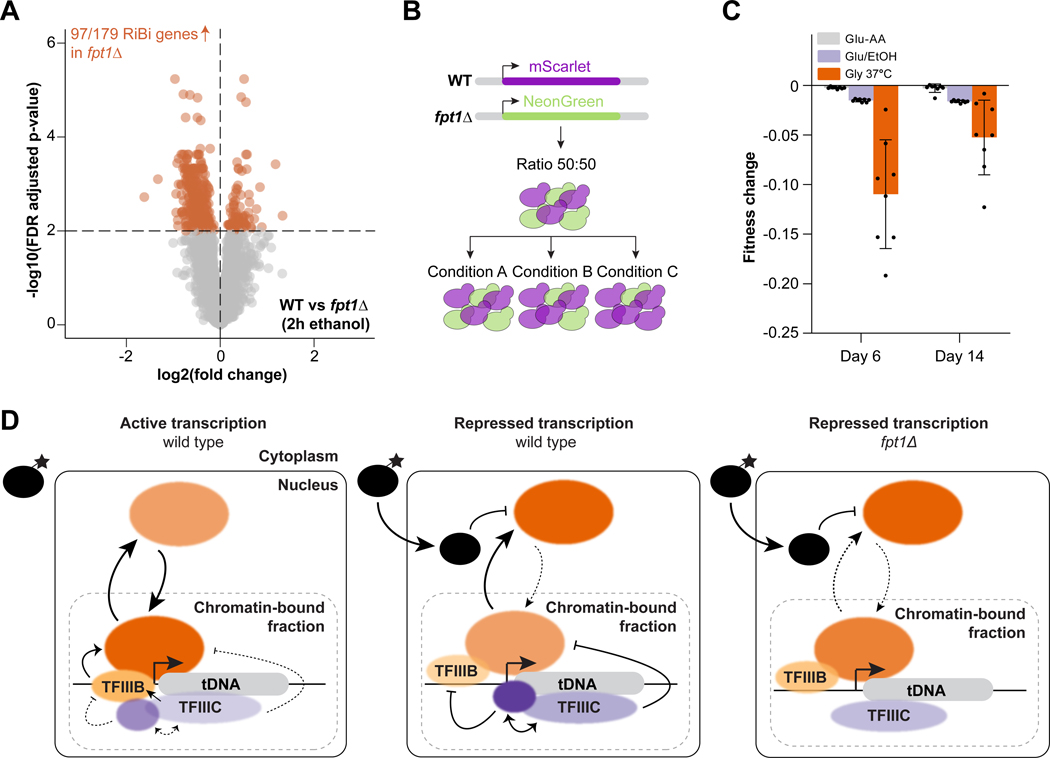
Figure 7. Fpt1 affects tuning of ribosome biogenesis genes and cellular fitness in repressive conditions.
(A) Differential gene expression in WT and fpt1Δ in ethanol 2h (n = 4): log2 fold change and FDR (p-value) for 4978 expressed genes. Colored dots represent significant differentially expressed genes (FDR ≤ 0.01). Upregulated genes in fpt1Δ compared to WT are depicted on the left (n = 313 genes), downregulated genes on the right (n = 92 genes). (B) Competitive growth assay: the fluorescent markers mScarlet and NeonGreen were inserted at a neutral intergenic locus in WT and fpt1Δ in both combinations. Red and green cells were mixed in a 50:50 ratio and subjected to different growth conditions to study the effect on the ratio WT and fpt1Δ cells. (C) Relative fitness defect, expressed with the Malthusian coefficient, of fpt1Δ compared to WT in glucose but with alternating levels of non-auxotrophic amino acids (Glu-AA), alternating carbon source (Glu/EtOH), and glycerol 37°C (Gly 37°C). Data of four biological replicates including a color-swap is shown (n = 8). (D) A model for chromatin-associated regulation of the tDNA transcription machinery. For details, see main text.