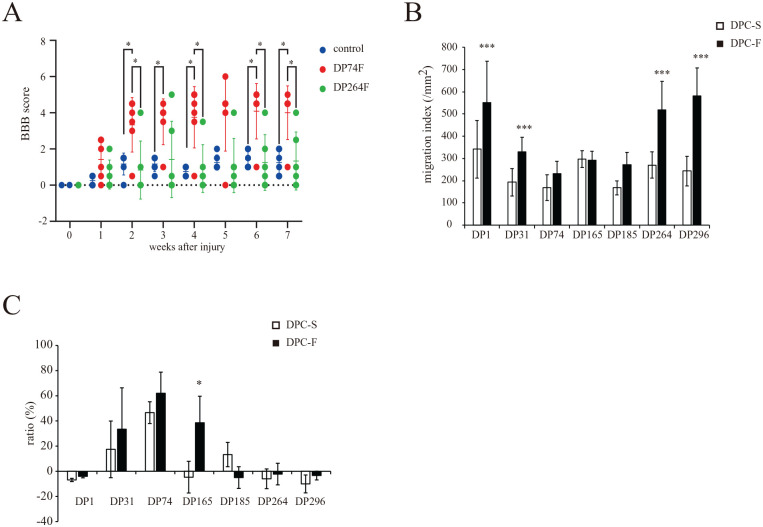
Figure 1.
Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2) priming on the properties of the seven individual donor-derived dental pulp cell (DPC) clones. (A) Effect of FGF2-primed DPC clone (DP74F or DP264F) transplantation on the locomotor function of rats with a completely transected spinal cord at the injury site. The locomotor function of the hind limbs was evaluated weekly for 7 weeks after injury. The values are expressed as individual scores with mean lines. Significant differences from the control group (rat with spinal cord injury with PBS injection) were determined using two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05; n = 6 for each group. (B) Effect of FGF2 priming on the cell migration indices of the individual donor-derived DPC clones (DPC-S and DPC-F; DPC clones primed without and with FGF2, respectively). The values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Significant differences from the FGF2 non-treated groups were determined using two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. ***P < 0.0001; n = 12 for each group. (C) Effect of FGF2 priming on the cell viability of 0.3 mM H2O2-treated individual donor-derived DPC clones. The values are expressed as the mean ± SD Significant differences from the FGF2 non-treated groups were determined using the two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05; N = 4 (n = 6) for each group.