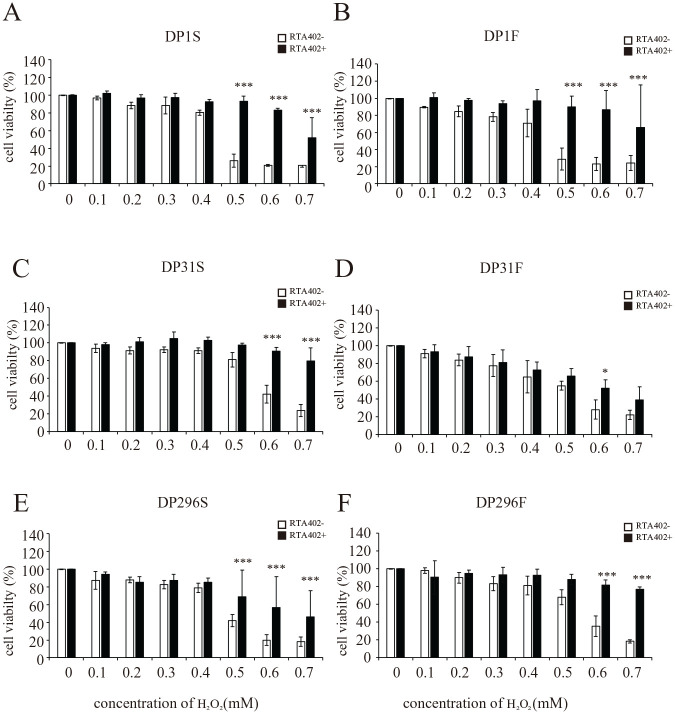
Figure 5.
Effect of RTA402 on the resistance to H2O2-induced cell death in individual donor-derived dental pulp cells (DPCs) [DPC-S and DPC-F; DPC clones primed without and with basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2), respectively]. After priming with/without FGF2 and treatment with/without 150 nM RTA402, each DPC clone (A, B: DP1; C, D: DP31; and E, F: DP296) was exposed to H2O2 at various concentrations (0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, and 0.7 mM) for 24 h, followed by the MTT assay. The ratios of the absorbance values recorded for the DPCs exposed to H2O2 were calculated relative to the control (neither H2O2- nor RTA402-treated DPCs). The values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Significant differences between the two groups were determined by two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001 vs DPC without RTA402 treatment with H2O2 at the same concentration; N = 3 (n = 6) for each group.