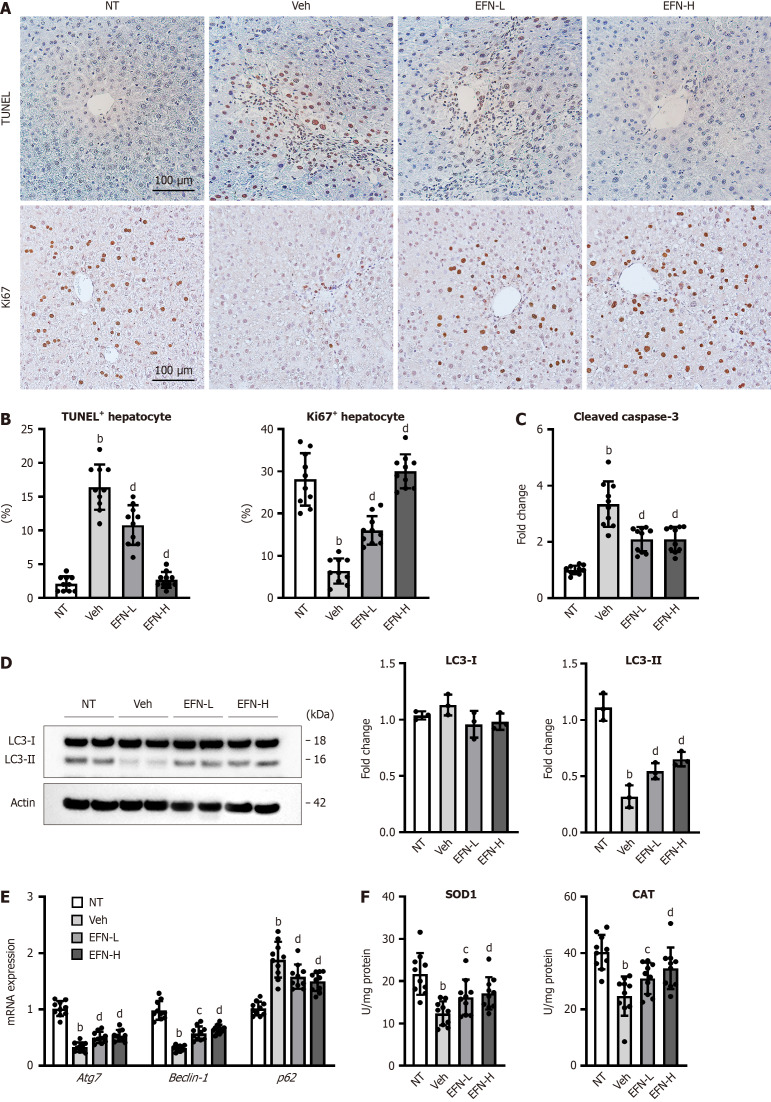
Figure 2.
Elafibranor on hepatocyte cell death, autophagy and oxidative stress in the alcohol-associated liver disease mice. A: Representative microphotographs of TdT-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) and Ki67 staining of the livers in the experimental mice; B: Quantification of TUNEL-positive hepatocytes and Ki67-positive hepatocytes in high-power field (n = 10); C: Cleaved caspase-3 level in the liver tissue (n = 10); D: Western blot for LC3-1 and 2 protein level in the liver tissue. Actin was used as an internal control (n = 3); E: Hepatic mRNA level of the markers related to autophagy (n = 10); F: Hepatic level of antioxidant enzymes, superoxide dismutase 1 and catalase (n = 10). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as an internal control for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (E and F). Quantitative values are indicated as fold changes to the values of non-therapeutic group (C-E). Data are the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs non-therapeutic group; cP < 0.05 vs vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; dP < 0.01 vs vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group, significant difference between groups by Student’s t-test. NT: Non-therapeutic group; Veh: Vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; EFN-L: Elafiblanor (3 mg/kg/day)-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; EFN-H: Elafibranor (10 mg/kg/day)-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; TUNEL: TdT-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase.