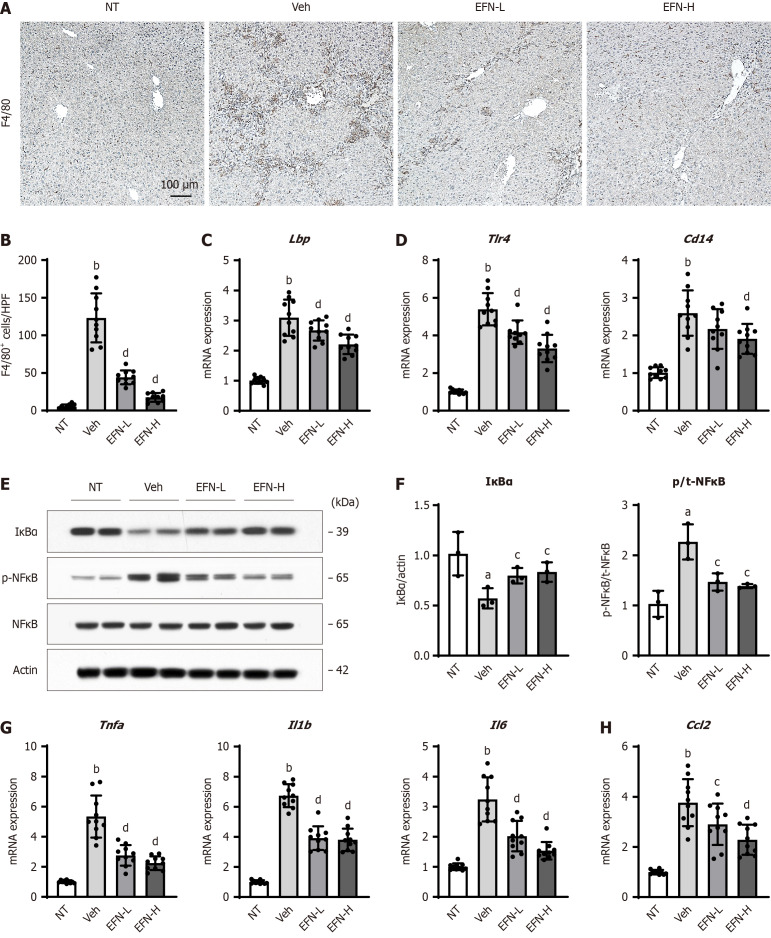
Figure 5.
Elafibranor on Kupffer cell-mediated inflammatory response in the alcohol-associated liver disease mice. A: Representative microphotographs of F4/80 staining of the livers in the experimental mice; B: Quantification of F4/80-positive cells in high-power field (n = 10); C and D: Hepatic mRNA level of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (C), toll like receptor 4 and CD14 (D) (n = 10); E: Western blot for the protein expression of IκBα, p-nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) and NF-κB in the liver tissue. Actin was used as an internal control; F: Quantification of the protein level of IκBα and the ratio of NF-κB phosphorylation based on western blotting (n = 10); G and H: Hepatic mRNA level of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin 1β (Il1b), and Il6 (G), and Ccl2 (H) (n = 10). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as an internal control for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (C, D, G and H). Quantitative values are indicated as fold changes to the values of non-therapeutic group. Data are the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs non-therapeutic group; bP < 0.01 vs non-therapeutic group; cP < 0.05 vs vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; dP < 0.01 vs vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group, significant difference between groups by Student’s t-test. NT: Non-therapeutic group; Veh: Vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; EFN-L: Elafiblanor (3 mg/kg/day)-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; EFN-H: Elafibranor (10 mg/kg/day)-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; Lbp: Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein; TLR: Toll like receptor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin.