Fig. 7 |. Ischemic injury is not necessary and mechanical trauma is sufficient to elicit BZ biology.
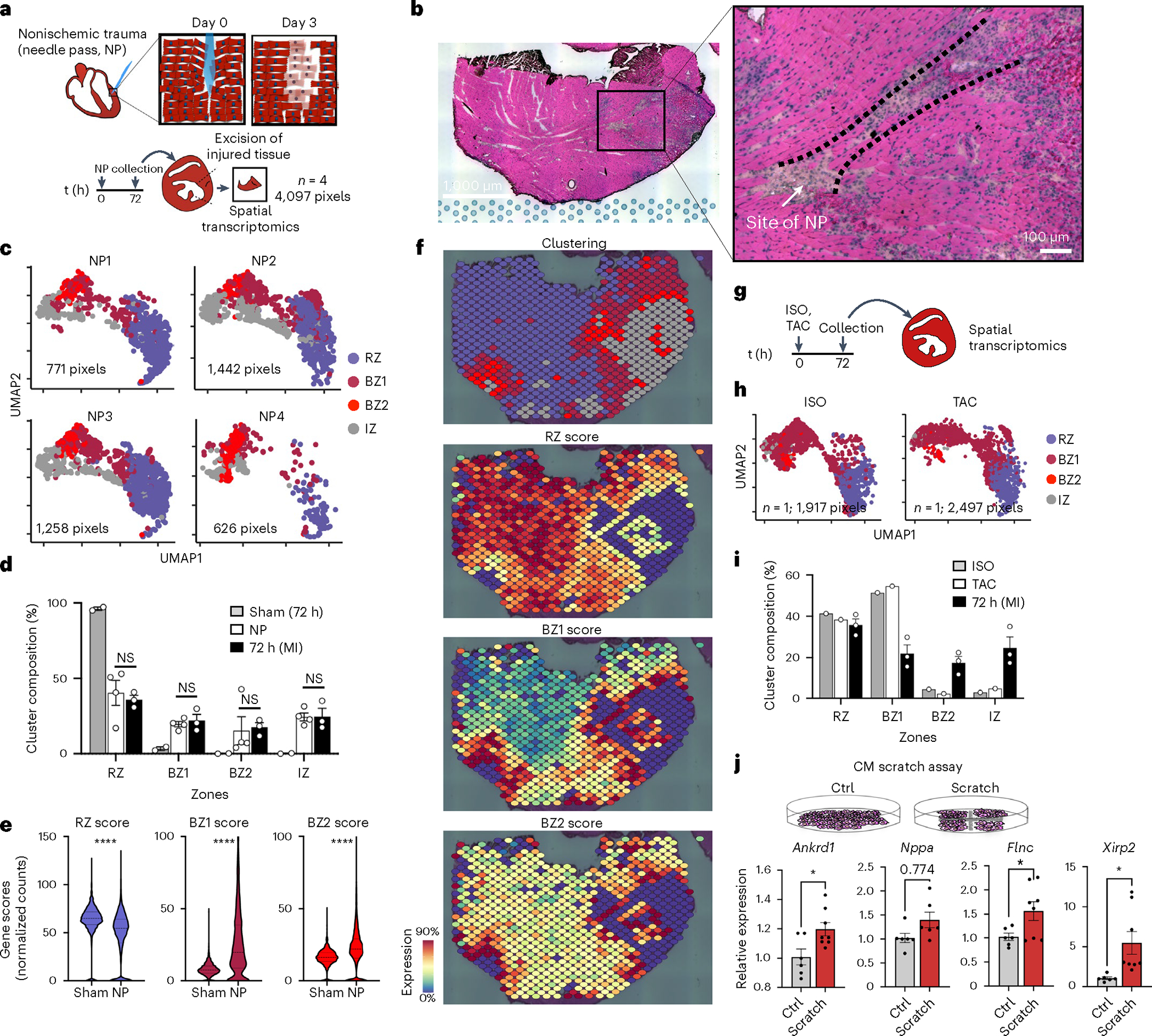
a, To induce nonischemic, mechanical trauma in the heart, we subjected hearts to NP (see Methods for full details), collected tissue 72 h after injury and excised the injured section of the left ventricle for spatial transcriptomics (n = 4; 4,097 pixels). b, The site of NP injury was identified in the H&E-stained sections by immune infiltrate and disrupted myocyte bundles. Representative image of four separate experiments. c, UMAP plots of each NP replicate in the same integrated space as the permanent ligation samples. d, Bar plots comparing the cluster composition of NP (n = 4) to sham (n = 2) and 72 h post-MI (n = 3) samples. e, Violin plots of RZ, BZ1 and BZ2 scores comparing sham to NP injury (all samples combined; median and 25th–75th percentile demarcated with dashed lines). f, Spatial plots showing BZ1 and BZ2 signatures (top, clustering; bottom, gene-set scores) surrounding the site of injury. g, Mice were subjected to either ISO treatment (n = 1) or TAC (n = 1) and collected for spatial transcriptomics after 72 h. h, UMAP plots of ISO and TAC samples in integrated space with i cluster composition quantified below (percentage of total pixels per sample, n = 1). j, Scratch assay was performed on confluent cultures of NRVMs seeded on 6-well plates; RNA was isolated from cultured cells 24 h after the scratch assay was performed. The BZ genes Ankrd1 (P = 0.0196), Flnc (P = 0.0394) and Xirp2 (P = 0.0212) were significantly increased in scratched NRVMs compared to unscratched Ctrl plates (n = 6, Ctrl; n = 8, scratch); Nppa did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.0774). d,i,j, Data are presented as mean values ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001. d,j, Unpaired Student’s t-test. e, Mann–Whitney U-test.
