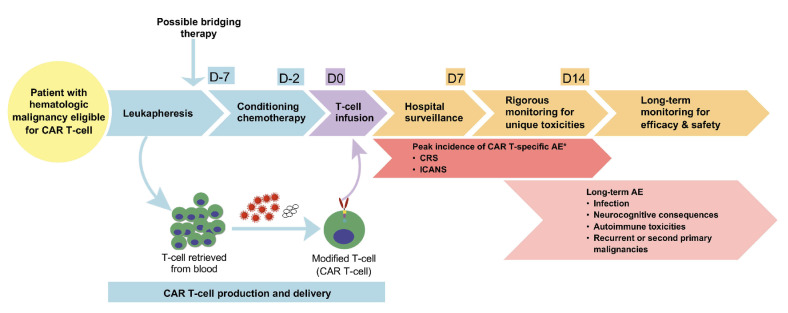
Figure 1.
Treatment and monitoring of patients receiving chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. T cells are collected from the patient through leukapheresis and modified in vitro by the addition of the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) vector. The modified CAR T cells are later infused back after the patient has received conditioning chemotherapy during the week prior to infusing the CAR T cells. This conditioning therapy, also known as lymphodepletion therapy, typically includes fludarabine and/or cyclophosphamide. Patients who receive CAR T-cell therapy should be hospitalized for a minimum of 1 week after the infusion, as recommended by the CAR-T-cell Therapy Associated Toxicity (CARTOX) working group or benefit from equivalent monitoring depending on the different local organizations in the world. *Cytokine release syndrome and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome usually appear within the first 2 weeks after CAR T-cell infusion.4 CAR: chimeric antigen receptor; D: day; AE: adverse events; CRS: cytokine release syndrome; ICANS: immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome.