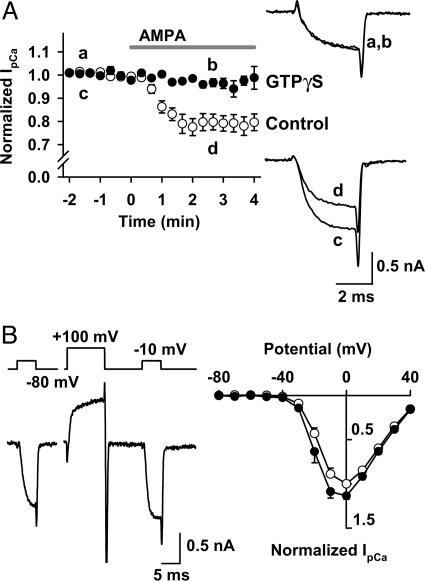
Fig. 4.
AMPAR-dependent IpCa inhibition involves heterotrimeric G proteins. IpCa was evoked by a depolarizing test pulse stepping to 0 mV. CTZ (100 μM) was present throughout. (A) GTPγS (0.2 mM) loaded into the presynaptic terminal from the patch pipette blocked the AMPA-induced IpCa inhibition. Sample records are averaged IpCa before (traces a and c) and during (traces b and d) application of AMPA, with (a and b) or without (c and d) GTPγS. Data points and bars indicate mean ± SEM (n = 5 each). (B) Voltage-dependent disinhibition of IpCa. In the presence of AMPA (10 μM), IpCa was evoked by pulses (5 ms) stepping to various potentials before and 10 ms after a conditioning pulse stepping to +100 mV for 10 ms. (Left) Command voltage protocol (Upper) and IpCa (Lower). (Right) Current-voltage relationships of IpCa before (filled circles) and after (open circles) the conditioning pulse. Data are derived from five calyces.