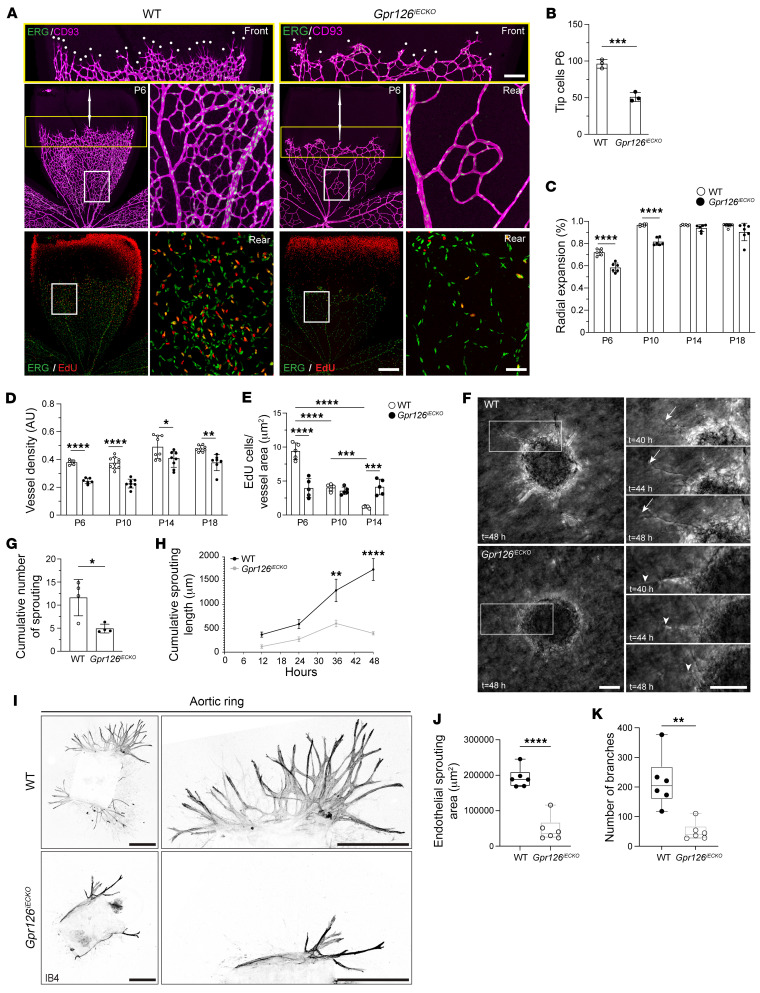
Figure 4. GPR126 is required for angiogenesis in the retina and in the brain.
(A) Confocal images of CD93 (magenta, ECs), ERG (green, EC nuclei), and EdU (red, proliferation) in WT and Gpr126iECKO mouse retinas at P6 show retinal vessels at the petal, front, and rear regions. White dots highlight tip cells. Scale bars: petal, 500 μm; rear, 100 μm; front, 250 μm. (B) Tip cell quantification in the yellow rectangle in A (n = 3 WT, n = 3 Gpr126iECKO retinas). (C) Retinal vasculature radial expansion at P6, P10, P14, and P18 in WT and Gpr126iECKO mice (n = 6–8 WT, n = 6–7 Gpr126iECKO retinas). (D) Postnatal retinal vessel density (P6, P10, P14, P18) in WT and Gpr126iECKO mice (n = 5–10 WT, n = 6–9 Gpr126iECKO retinas). (E) EdU-positive ECs/μm2 of vessel area postnatally (P6, P10, P14, P14) in WT and Gpr126iECKO retinas (n = 5 WT, n = 5 Gpr126iECKO retinas). (F) Phase-contrast images of sprouting spheroids from fBECs of WT and Gpr126iECKO mice at P18 after stimulation with VEGF (80 ng/mL) and FGFb (50 ng/mL). Right: Magnified images at t = 40, 44, and 48 hours (for time-lapse, see Supplemental Video 1). Arrows, sprouting ECs; arrowheads, retracting ECs. Scale bars: 40 μm. (G) Cumulative sprouts per spheroid of WT (n = 16) and Gpr126iECKO (n = 16) fBECs. Each symbol represents an experiment (n = 4 WT, n = 4 Gpr126iECKO mice). (H) Cumulative sprouting lengths per spheroid of WT (n = 12) and Gpr126iECKO (n = 12) fBECs after 12, 24, 36, and 48 hours (n = 6 WT, n = 6 Gpr126iECKO mice). (I) Aortic rings from WT and Gpr126iECKO mice show vascular sprouts (magnified) via IB4 immunostaining. Scale bars: 500 μm. (J and K) Endothelial sprouting area (J) and branch numbers (K) as depicted in I (n = 6 WT, n = 6 Gpr126iECKO mice). Data are shown as means ± SD. (B–D, G, J, and K) Unpaired t tests with Welch’s correction; (E and H) 2-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.