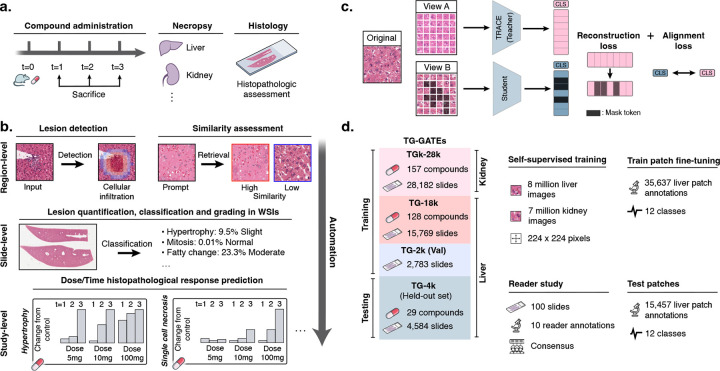
Figure 1: Preclinical AI-enhanced safety assessment.
a. Before entering human clinical trials, compounds must undergo a preclinical safety assessment on rodents to assess their potential toxicity. b. Preclinical histopathological drug safety studies can benefit from AI assistance and automation at different scales: at region-level to detect and retrieve certain morphologies and lesions, at slide-level to automatically quantify and score abnormal lesions in WSIs, and at study-level to automatically characterize the dose-time morphological response of the candidate compound. c. We train TRACE , a self-supervised vision encoder based on the Vision Transformer architecture trained to extract representative embeddings of small histopathological regions in Rattus norvegicus. TRACE uses iBOT training32 which combines a contrastive self-distillation objective33, and an image reconstruction objective31. d. TRACE is trained and evaluated on the TG-GATEs dataset. Data and annotation distribution used in this work. TG-GATEs: Toxicogenomics Project-Genomics Assisted Toxicity Evaluation System; WSI: Whole-Slide Image; AI: Artificial Intelligence; iBOT: Image BERT with Online Tokenizer.