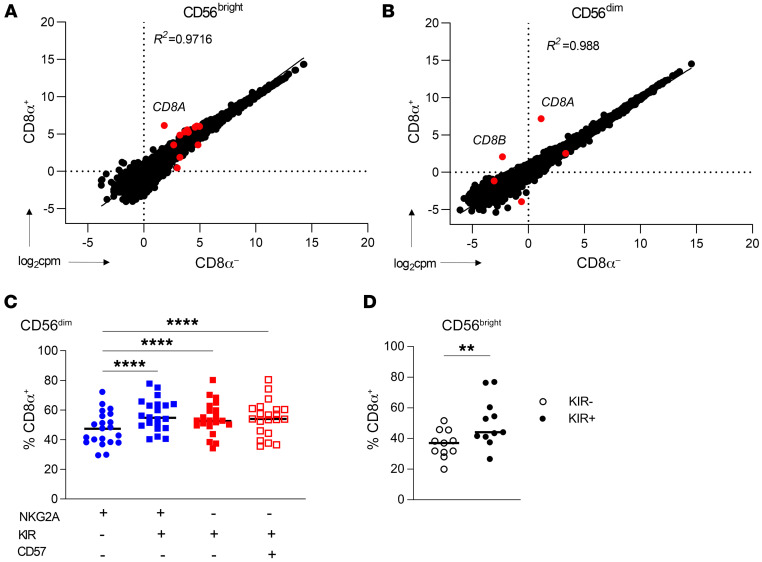
Figure 3. CD8α does not mark a distinct, terminally differentiated population.
(A and B) Bulk RNA-Seq was performed on freshly isolated (A) CD56bright or (B) CD56dim NK cells sorted on the basis of CD8α expression (CD3–CD19–CD14–). Data are shown as the log2-normalized expression of protein-coding genes in CD8α+/– cell populations. Red dots indicate genes that were statistically significantly differentially expressed (adjusted P < 0.05). n = 6 unique donors. The R2 value was derived from simple linear regression of gene expression data. (C and D). Peripheral blood NK cells were stained for the expression of markers of NK maturation. (C) CD56dim NK cell maturation stages were identified based on expression of NKG2A, KIR (KIR3DL1, KIR2DL1, and KIR2DL2/3), and CD57, with maturation increasing from left to right. Data are shown as the percentage of each subset that was positive for CD8α expression. n = 28 donors. (D) Expression of CD8α within NKG2A–CD56brightKIR– or KIR+ (KIR3DL1+, KIR2DL1+, and KIR2DL2/3+) NK cells. n = 11 donors. Data represent the mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001, by (C) 2-way ANOVA with Holm-Šídák correction for multiple comparisons and (D) paired, 2-tailed Student’s t test.