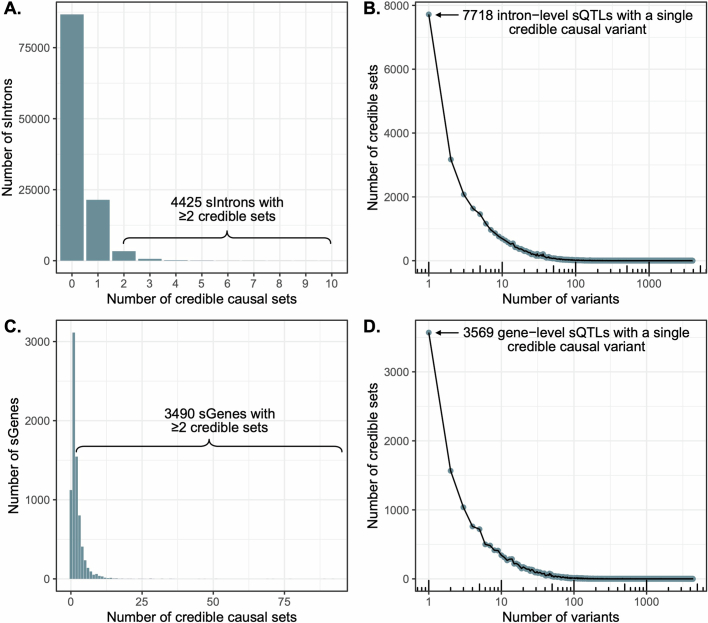
Extended Data Fig. 2. Mapping of high-resolution sQTLs.
(A) Number of credible sets per sIntron, where we define sIntrons as all introns (that passed filtering) for autosomal genes identified as sGenes in the FastQTL permutation pass. We ran SuSiE separately for each sIntron. (B) Resolution of sIntron fine-mapping, defined as the number of variants per credible set. (C) After fine-mapping, overlapping intron-level credible sets were iteratively merged to produce gene-level credible sets. Panel C shows the number of merged credible sets per sGene. (D) The resolution of sGene fine-mapping, defined as the number of variants per merged credible set. These results demonstrate evidence of widespread allelic heterogeneity whereby multiple causal variants independently modulate splicing patterns of the same genes.