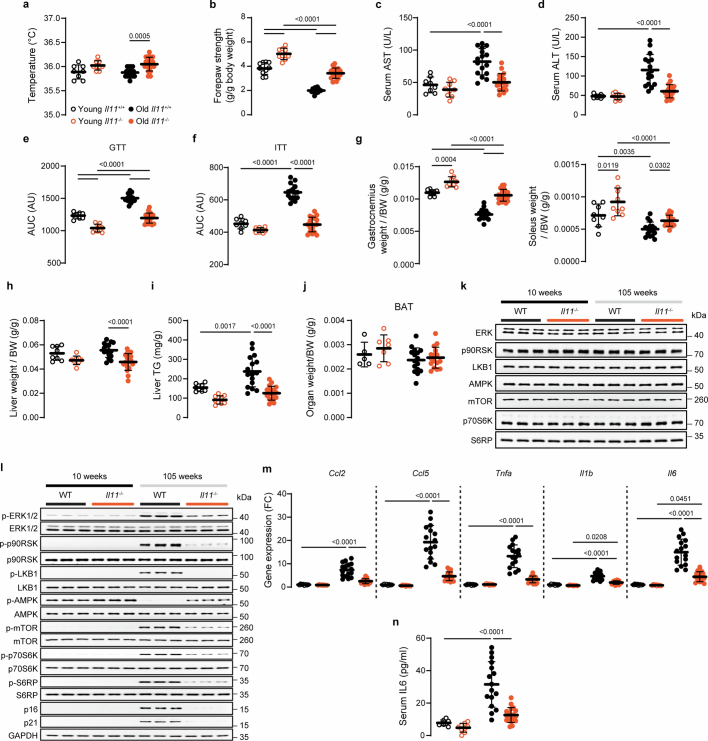
Extended Data Fig. 5. Female Il11−/− mice are protected from age-associated frailty and inflammation and have advantageous metabolic profiles.
a Body temperatures, b front paw grip strength, serum levels of c ALT, d AST, area under the curves (AUC) of e glucose tolerance tests (GTT) and f insulin tolerance tests (ITT), weights of g skeletal muscle (gastrocnemius and soleus) and h liver (normalised/indexed to BW), i liver triglyceride (TG) levels, j indexed brown adipose tissues (BAT) weight, k WB of total proteins for the respective phospho proteins in vWAT as shown in Fig. 2j,l WB showing ERK1/2, mTOR, p70S6K, and S6RP activation and p16, p21, and GAPDH protein expression levels (n = 6/group) in gastrocnemius, m relative pro-inflammatory gene expression (Ccl2, Ccl5, Tnfα, Il1β and Il6) levels in vWAT, and n serum IL6 levels from young (12-week-old) and old (105-week-old) female WT and Il11−/− mice. a-j, m-n Data are shown as mean ± SD, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s correction (young WT, n = 5 (j), n = 8 (a, c-i, m-n), n = 10 (b); young Il11−/−, n = 7 (j), n = 9 (a-i, m-n); old WT, n = 16; old Il11−/−, n = 16 (j), n = 18 (a-i, m-n). For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1. AU: arbitrary units; BW: body weight; FC: fold change.