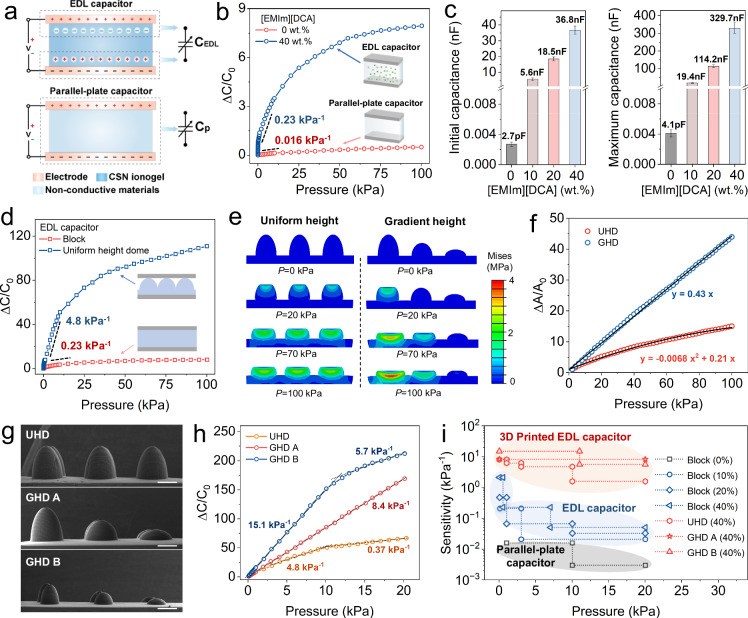
Fig. 4. Design and the sensing mechanism of the 3D printed capacitive sensor based on CSN ionogels.
a Sensing mechanisms of the parallel-plate capacitor (top) and the CSN ionogel-based EDL capacitor (bottom). b Comparison on the ΔC/C0 – P relation between the parallel-plate capacitor and the CSN ionogel-based EDL capacitor. c Comparisons on initial capacitance (under no external pressure) and maximum capacitance (under the pressure of 100 kPa) between the parallel-plate capacitor and the CSN ionogel-based EDL capacitors with different [EMIm][DCA] contents. d Comparisons on the ΔC/C0 – P relation of the 3D printed EDL capacitive sensors with block and dome-shaped CSN ionogel layers. e FEA simulation results for pressing the domes with uniform height and gradient height. f Comparisons on the ΔA/A0 – P relation between the three domes with uniform height and gradient height. g SEM images of the dome shaped CSN ionogels with uniform height and gradient height in different scales. Scale bar: 300 μm. h Comparison on the ΔC/C0 – P relation of the CSN ionogel capacitive sensors with the corresponding micro-architectures from (g). i Performance comparison on the sensitivity of the different capacitive sensors in this work. Data are presented as the mean values ± SD, n = 3 independent samples. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.