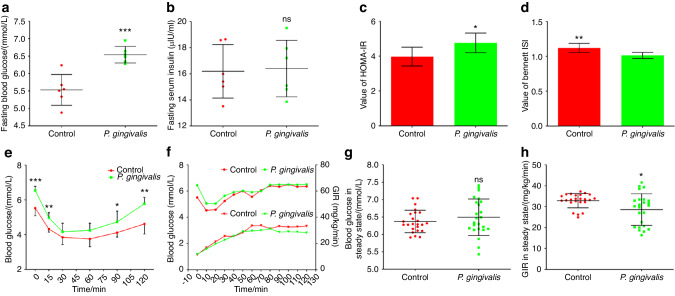
Fig. 3.
P. gingivalis may have functional effects on IR in vivo. Changes in fasting blood glucose (a) and fasting insulin (b) levels in mice orally administered P. gingivalis for 12 weeks (n = 6 in each group). Calculation of HOMA-IR (c) and ISI (d) based on fasting blood glucose and insulin measurements (n = 6 in each group). e Insulin tolerance test of mice orally administered P. gingivalis for 12 weeks (n = 6 at each time point). After oral feeding of P. gingivalis for 12 weeks, hyperinsulinaemic–euglycaemic clamp was performed to detect blood glucose levels (upper) and GIR (lower) at different time points in mice (f, n = 6 at each time point), and the differences in blood glucose levels (g) and GIR (h) in the steady state were compared. ISI insulin sensitive index, GIR glucose infusion rate, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, no significance