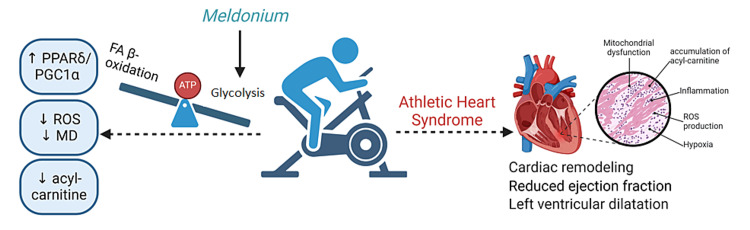
Figure 3. Cardioprotective effect of meldonium in hypoxic conditions induced by effort.
In athletes, prolonged efforts can cause athletic heart syndrome by promoting inflammation, ROS (reactive oxygen species) production, hypoxia, MD (mitochondrial dysfunction), and accumulation of acyl-carnitine. Meldonium inhibits carnitine metabolism and decreases FA β-oxidation (fatty acids beta-oxidation) in the mitochondria. At the same time, meldonium activates glucose metabolism by activating 6PF1K (6-phosphofructo-1-kinase) and pyruvate dehydrogenase and shifts the production of ATP in case of aerobic effort from lipids to carbohydrates. This mechanism of action for meldonium presents a favorable overall effect on the athletes’ heart.
PPARδ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta; PPAR-α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha.
Source: This image is the original work of the authors, and the image was created by BioRender.com.