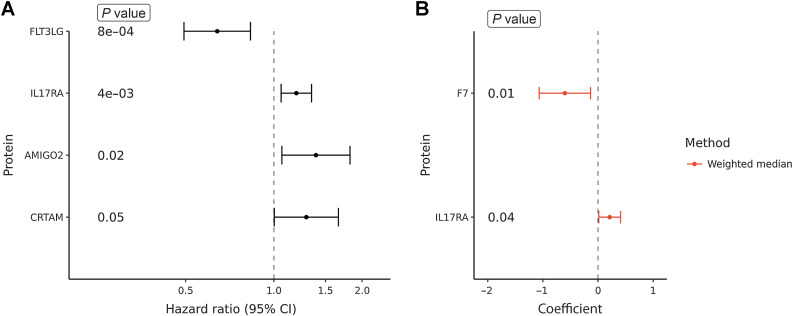
Figure 2.
Association between polygenic risk score (PRS) for plasma protein levels and MN in an independent subset of the UKBB (A). Association between global (i.e., genome-wide) PRS (PRSglobal-pQTL) for plasma protein levels and risk of MN. For each protein, PRSs for each individual were constructed by summing the product of the beta coefficients for the association between and the number of alternate alleles for each protein quantitative loci detected through a genome-wide interrogation. The beta coefficients were obtained from SNP-protein association analysis. Displayed are the hazard ratio and 95% confidence intervals for proteins in which genetically predicted levels were significantly associated with MN risk. B, Two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses of the causal impact of plasma protein levels on MN risk. Each dot represents the estimated MR effect for the corresponding protein with the corresponding 95% confidence interval.