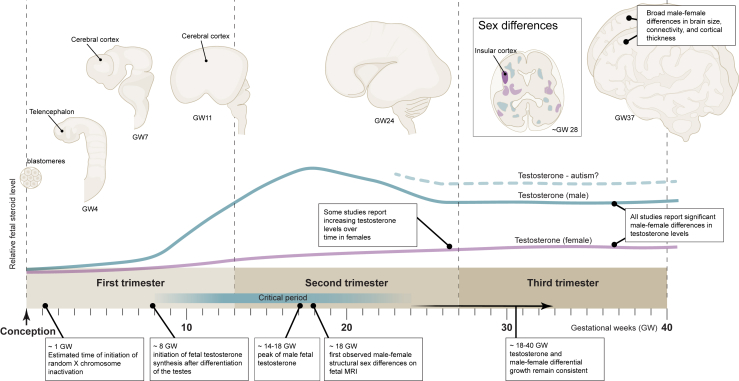
Figure 1.
Timeline of human brain development from conception to birth showing human brain morphology over developmental time (top), predicted testosterone dynamics (middle), and key events in sex-biased development (bottom). The box shows an axial section with examples of regions with growth trajectory (blue, male-biased; purple, female-biased) sex differences found in fetal MRI (141). The insular cortex is an example of a focal region that was larger in males than in females. The sex chromosomes begin exerting sex-specific effects soon after conception. Testosterone is given here as a classic example of a steroid sex hormone with levels that differ by sex. Fetal testosterone increases after the differentiation of the testes in males. Male testosterone is thought to peak between GW14 and GW18 and then remain relatively consistent (141). Studies have generally reported higher male testosterone, and some studies have reported increasing testosterone in females over time (142). GW, gestational week; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.