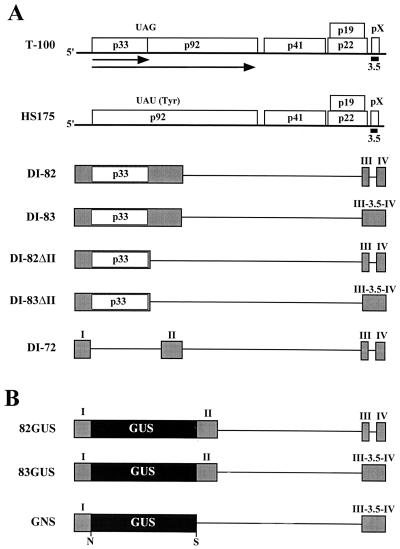
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic representation of TBSV genome and various defective viral RNAs. The wild-type TBSV genome (T-100) is shown at the top as a thick horizontal line, with coding regions depicted as boxes which include the approximate molecular masses (in thousands) of the encoded proteins (16). The translation product p33 and its readthrough product p92 are presented as arrows below the genome, and the approximate position of region 3.5 is shown as a small black box near the 3′ end of the genome (labeled 3.5). HS175 is a mutant of the genome in which the p33 termination codon has been replaced by a tyrosine codon so as to allow for expression of p92 but not p33 (33). Below, various smaller defective viral RNAs are depicted; shaded boxes correspond to regions of the genome retained in these molecules, whereas thin horizontal lines correspond to genomic segments which are absent. DI-82 and DI-83 both encode p33 (open box) and are identical except that region 3.5 is absent in DI-82 (42). DI-82ΔII and DI-83ΔII are derivatives of DI-82 and DI-83, respectively, in which a segment, which includes region II, is deleted. DI-72 represents a prototypical DI RNA and is composed of four noncontiguous regions of the genome (i.e., regions I through IV) (42). (B) Schematic representation of GUS-virus hybrid mRNAs with the GUS coding region depicted as a black box. 82GUS and 83GUS are identical except for the absence of region 3.5 in the former. GNS is a derivative of 83GUS which lacks region II and contains introduced NcoI (N) and SacI (S) sites.