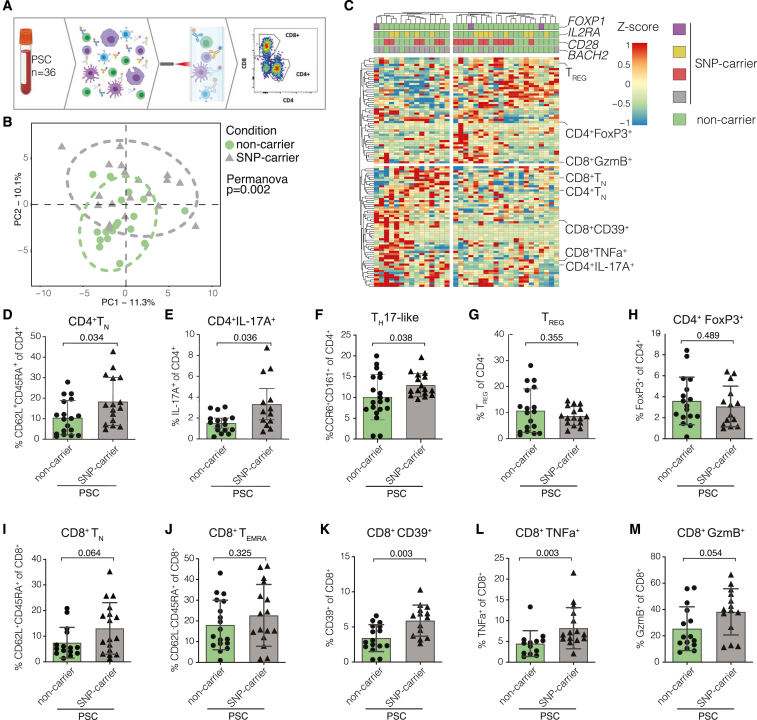
Figure 1.
Risk variant rs56258221 (BACH2/MIR4464) entails phenotypic differences in peripheral T cells in people with PSC
(A) Schematic depiction of the workflow for immunophenotyping.
(B) Principal component analysis of the analyzed immunophenotyping data, separated by the genotype for polymorphism rs56258221.
(C) Heatmap illustrating the immunophenotyping dataset (n = 36) and highlighting populations that differed in frequency between carriers of rs56258221 (n = 18) and non-carriers (n = 18).
(D–H) Frequencies of different CD4+ T cell subsets. (D) TN, identified by CD62L/CD45RA. (E) TH17 cells identified by IL-17A expression upon stimulation with PMA (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate)/ionomycin. (F) TH17 cells identified by CCR6/CD161. (G) TREG identified by CD127/CD25. (H) TREG identified by FoxP3 expression upon stimulation with PMA/ionomycin.
(I–M) Frequencies of different CD8+ T cell subsets. (I) TN, identified by CD62L/CD45RA. (J) TEMRA, identified by CD62L/CD45RA. (K) CD39 expression on CD8+ T cells. (L) TNF expression upon stimulation with PMA/ionomycin. (M) GzmB expression upon stimulation with PMA/ionomycin. Characteristics of the clinical cohort are included in Table S1. Statistics: normality distribution was tested by Kolmogorov-Smirnov test; normal distribution: Welch’s t test; no normal distribution: Mann-Whitney U test. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data are presented as mean ± SD and deriving from n ≥ 2 repeats per experiment.