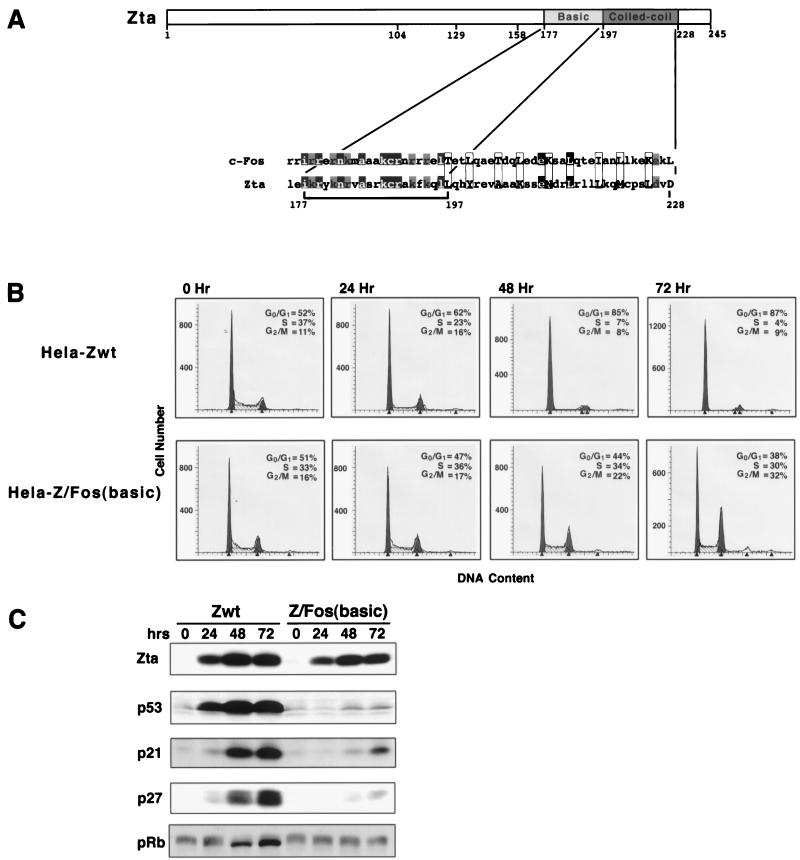
FIG. 2.
The DNA binding domain of Zta is required for induction of p21, p27, and p53 and growth arrest. (A) Schematic representation of Zta structure and alignment of Zta and c-Fos basic/dimerization domains. The bracket indicates the region of Zta which is replaced in the Z/Fos(basic) domain swap mutant. Black boxes indicate homologous amino acids, and gray boxes indicate related amino acids. The aligned 3-4 repeats of hydrophobic residues for c-Fos and Zta are enclosed by rectangles. (B and C) Cell cycle analysis (B) and Western blot analysis of the cell cycle regulatory proteins p53, p21, p27, and pRb (C) following induction of the indicated Zta proteins in stably transfected HeLa cells. Cell lines were generated simultaneously, and induction experiments were performed in parallel. Cells were expanded in the presence of tetracycline (2 μg/ml). Cells were then trypsinized, washed twice with 1× PBS, and either collected (for 0-h time point) or plated in medium with no tetracycline for the indicated times. A portion of collected cells were stained with propidium iodide and subjected to FACS analysis to determine the DNA content (B). (C) The remaining cells were suspended in Laemmli buffer and boiled for 20 min to reduce the viscosity of the samples. A portion of these samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and subjected to sequential Western blot analysis (with a stripping step between probings) using anti-hemmagglutinin (HA) (HA11.1; Boehringer Mannheim) (to detect HA-tagged Zta proteins), anti-p53 (DO-1; Santa Cruz), anti-p21 (C19G; Santa Cruz), anti-Kip1/p27 (Transduction Laboratories), and anti-pRb (G3-245; PharMingen) antibodies. wt, wild type.