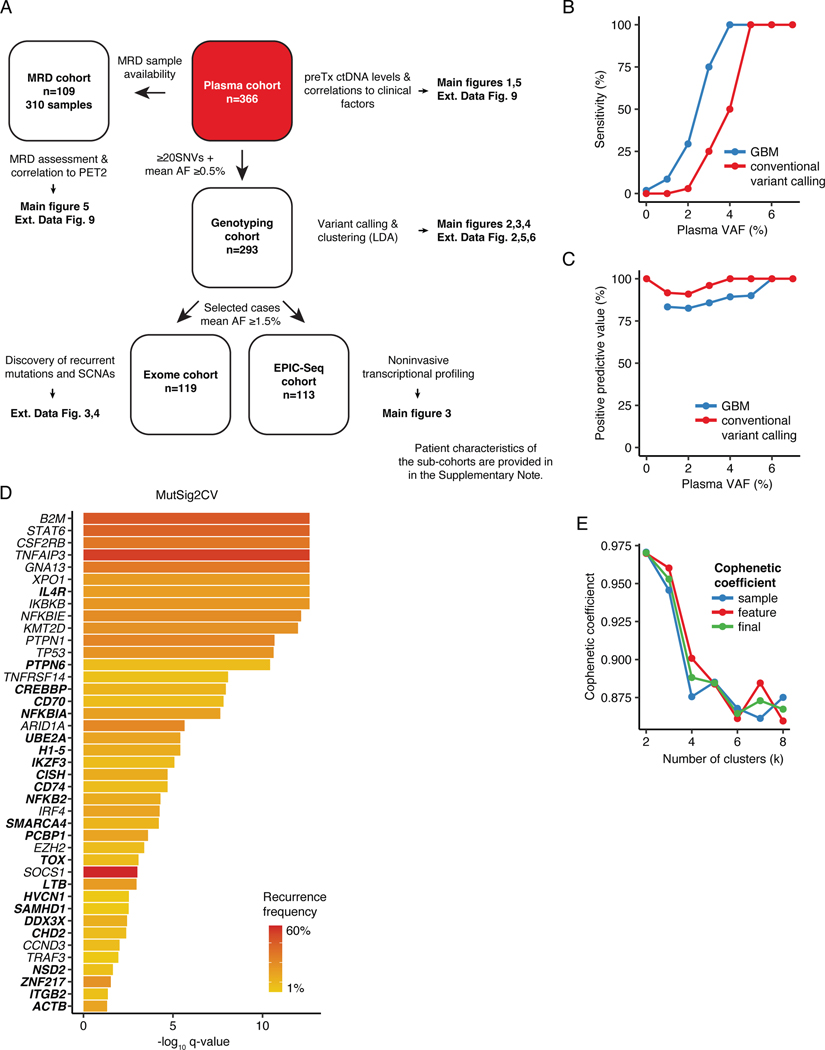
Extended Data Figure 1: Noninvasive profiling of cHL.
(A) Study overview. MRD: Minimal residual disease; PET2: Positron emission tomography after 2 cycles of chemotherapy; preTx: pretreatment; AF: allelic fraction; SNV: single nucleotide variants; LDA: Latent Dirichlet Allocation; SCNA: somatic copy number aberration; EPIC-Seq: epigenetic expression inference from cell-free DNA-sequencing. (B) Line plot summarizing sensitivity of the Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) model to call exome-wide SNVs as a function of plasma VAF in 2 non-Hodgkin lymphoma validation samples as compared with a conventional workflow. Sensitivity was calculated considering mutations with VAFs ranging from x-1 to x+1%. Tumor mutation calls were considered ground truth for sensitivity estimation. (C) Line plot summarizing positive predictive values (PPV) of the GBM model as a function of plasma VAF in 2 non-Hodgkin lymphoma validation samples as compared with a conventional workflow. PPV was calculated considering mutations with VAFs ranging from x-1 to x+1%. The union of tumor and deep plasma exome mutation calls were considered ground truth for PPV estimation. (D) Bar plot summarizing MutSig2CV -log10 q-values of 41 genes found to be significantly mutated in targeted or whole exome sequencing (q-value <0.05). The heat of the bars reflects mutation recurrence frequency. Genes that have not been recurrently described in the cHL literature (i.e. ≤1 study comprising at least 50 patients) are highlighted in bold. (E) Cophenetic coefficients (sample, feature and final) by number of clusters (k) when applied to the Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) framework to identify genetic subtypes in 293 cHL cases.