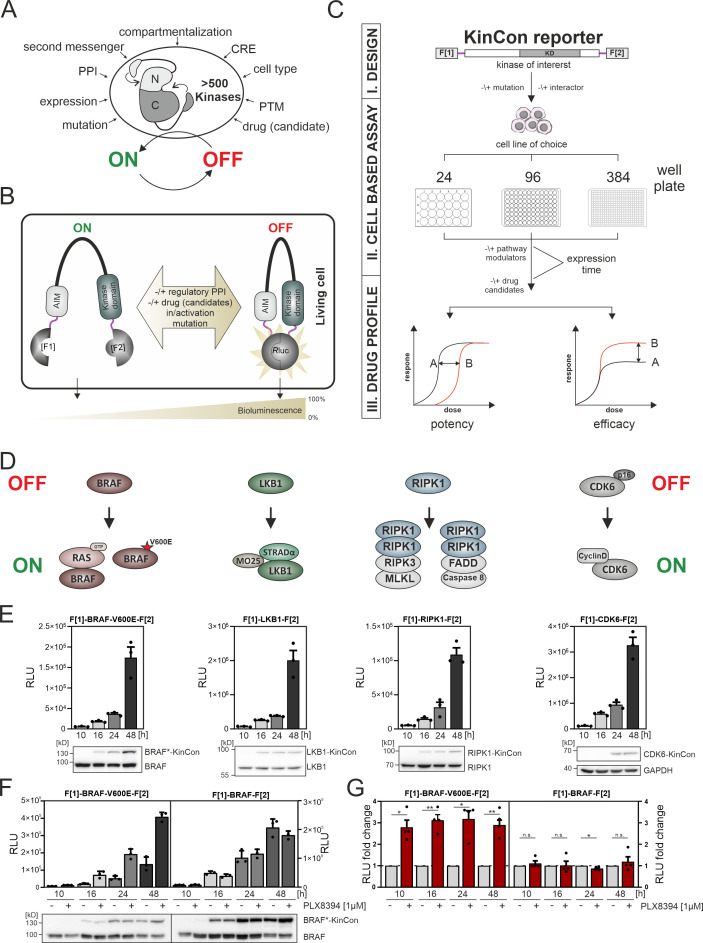
Figure 1. Kinase regulation and kinase conformation (KinCon) reporter technology features.
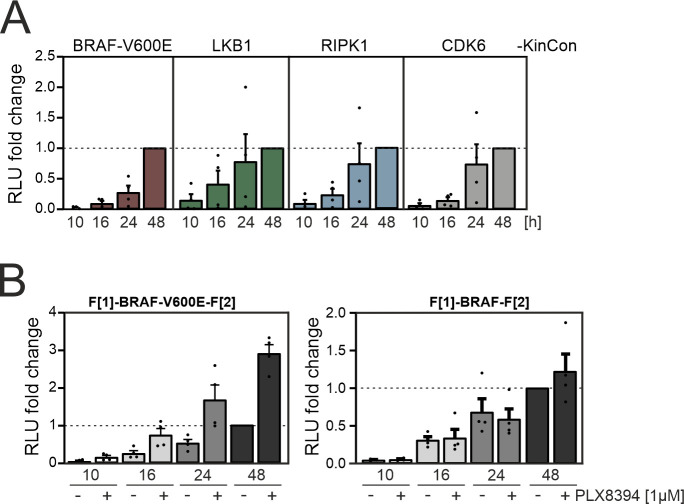
(A) Impact of indicated factors/features (e.g. protein-protein interactions [PPIs], post-translational modifications [PTM], cis-regulatory elements [CRE]) on the switch-like behavior of kinases. (B) Schematic representation of the KinCon reporter technology using the Renilla luciferase (RLuc) protein-fragment complementation assay (PCA) as it applies to kinases such as BRAF which contain auto-inhibitory modules (AIM); RLuc fragments 1 and 2 are N and C terminally fused to the kinase of interest (with interjacent linker in red) and are labeled with F[1] and F[2]. PPIs, drug (candidate) or small molecule binding, mutations and/or PTMs may convert the KinCon reporter into different conformation states. Protein movements are quantified through measuring alterations of bioluminescence signals upon RLuc substrate addition. (C) Shown is the workflow for the KinCon reporter construct engineering and analyses using KinCon technology. The kinase gene of interest is inserted into the multiple cloning site of a mammalian expression vector which is flanked by respective PCA fragments (F[1]-, -F[2]; KD, kinase domain) and separated with interjacent flexible linkers. Expression of the genetically encoded reporter in indicated multi-well formats allows to vary expression levels and define a coherent drug treatment plan. Moreover, it is possible to alter the kinase sequence (mutations) or to co-express or knock down the respective endogenous kinase, interlinked kinases, or proteinogenic regulators of the respective pathway. After systematic administration of pathway modulating drugs or drug candidates, analyses of KinCon structure dynamics may reveal alterations in potency, efficacy, and potential synergistic effects of the tested bioactive small molecules (schematic dose-response curves are depicted). (D) Simplfied schematic representation of the activation mechanisms of BRAF, LKB1, RIPK1, and CDK6 complexes (with indication of selected regulators or complex components) engaged in altering OFF (top) or ON (bottom) kinase states. (E) Representative KinCon experiments of time-dependent expressions of indicated KinCon reporter constructs in HEK293T cells are shown (mean ± SEM). Indicated KinCon reporters were transiently over-expressed in 24-well format in HEK293T cells for 10 hr, 16 hr, 24 hr, and 48 hr each. Immunoblotting show expression levels of endogenous kinases and over-expressed KinCon reporters. (F) Impact of 1 μM PLX8394 exposure (for 1 hr) on BRAF and BRAF-V600E KinCon reporters (HEK293T cells) is shown. Representative experiment of n=4 independent is presented. (G) RLuc PCA values have been normalized on the untreated conditions. The mean ± SEM of PLX8394 exposure on BRAF conformation opening and closing of n=4 experiments is shown. RLU, relative light units. Statistical significance for G: one-sample t-test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001).