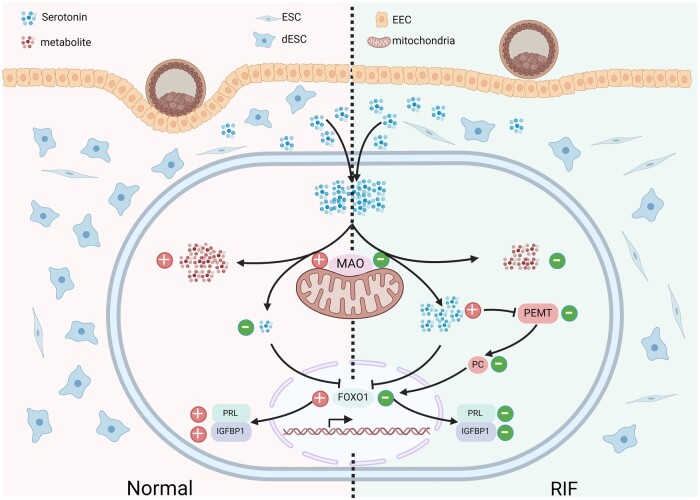
Figure 11.
Schematic representation of the role of monoamine oxidase in regulating decidualization in patients with recurrent implantation failure and fertile controls. The serotonin metabolic pathway is impaired due to attenuated MAO in the endometrial stromal cells of patients with RIF. Excessive serotonin leads to a decrease in FOXO1 as well as the decidualization markers PRL and IGFBP1. Attenuated MAO or excessive serotonin induces a decrease in PEMT, a gene related to phospholipid metabolism, and a corresponding decrease in PC. Exogenous PC upregulates FOXO1 and induces an increase in PRL and IGFBP1. RIF, recurrent implantation failure; ESC, non-decidualized endometrial stromal cells; dESC, decidualized endometrial stromal cells; EEC, endometrial epithelial cells; MAO, monoamine oxidase; PRL, prolactin; IGFBP1, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1; FOXO1, forkhead box O1; PEMT, phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase; PC, phosphatidylcholine.