Figure 4.
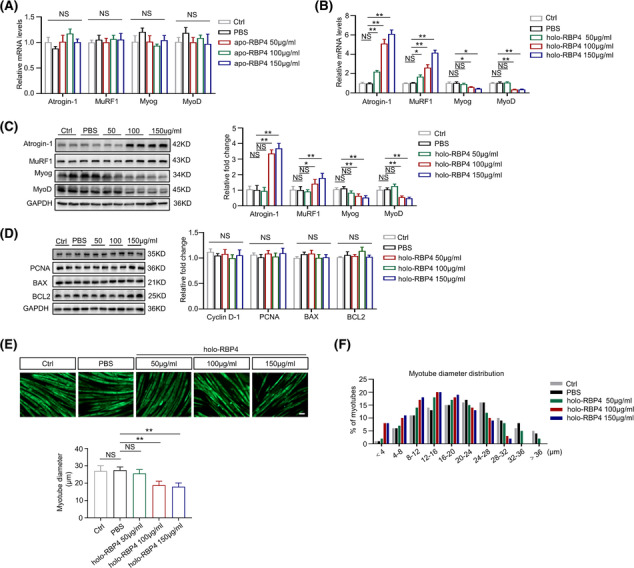
RBP4 induces muscle atrophy in C2C12 myotubes. C2C12 myoblasts were incubated with differentiation medium until cell fusion and then treated with retinol‐free RBP4 (apo‐RBP4) or retinol‐bound RBP4 (holo‐RBP4). (A) The mRNA levels of muscle atrophy marker Atrogin‐1 and MuRF1 as well as myogenic regulator MyoD and MyoG in C2C12 myotubes treated with apo‐RBP4. (B) The mRNA levels of muscle atrophy marker Atrogin‐1 and MuRF1 as well as myogenic regulator MyoD and MyoG in C2C12 myotubes treated with holo‐RBP4. (C) The protein levels of muscle atrophy marker Atrogin‐1 and MuRF1 as well as myogenic regulator MyoD and MyoG in C2C12 myotubes treated with holo‐RBP4. (D) The protein levels of proliferation marker PCNA and CCND1 as well as apoptosis marker Bax and Bcl‐2 in C2C12 myotubes treated with holo‐RBP4. (E) Representative immunofluorescence staining of myotubes with MHC (green, upper) and myotube diameters of C2C12 myotubes treated with holo‐RBP4. Scale bar = 50 μm. (F) Distribution of myotube with different diameter in C2C12 myotubes treated with holo‐RBP4. n = 6 per group, Ctrl, control. One‐way ANOVA analyses with post‐hoc correlation were used. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; NS, no significance.
