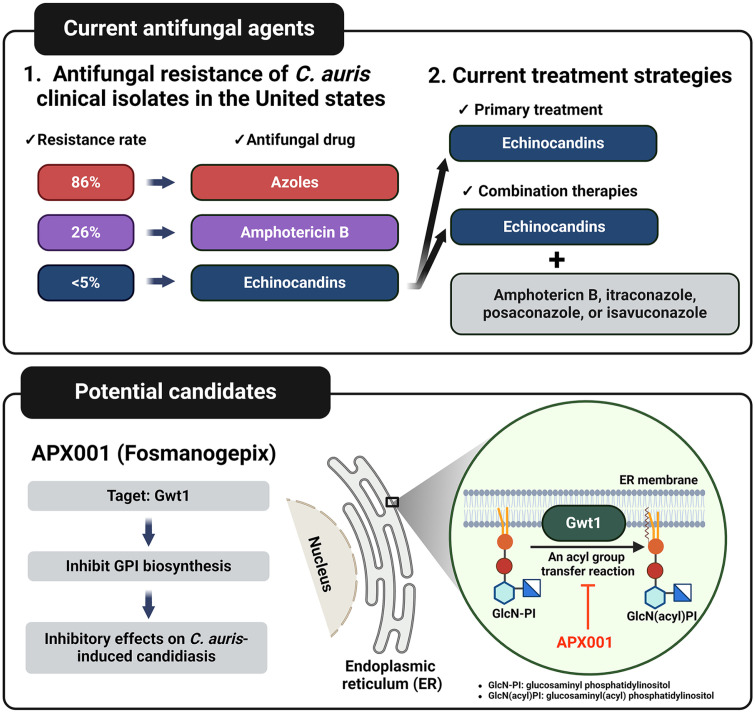
Fig. 5. Antifungal resistance of C. auris and candidiasis Treatment.
86% of C. auris isolates show resistance to azoles, while 26% are resistant to amphotericin B. Due to low levels of echinocandins resistance, initial treatment typically involves echinocandins use. Combining echinocandins with other antifungal agents like amphotericin B, itraconazole, posaconazole, or isavuconazole has been suggested. APX0001, targeting Gwt1 to inhibit GPI biosynthesis, shows promise as a novel antifungal medication against candidiasis. This figure was made using a Biorender.