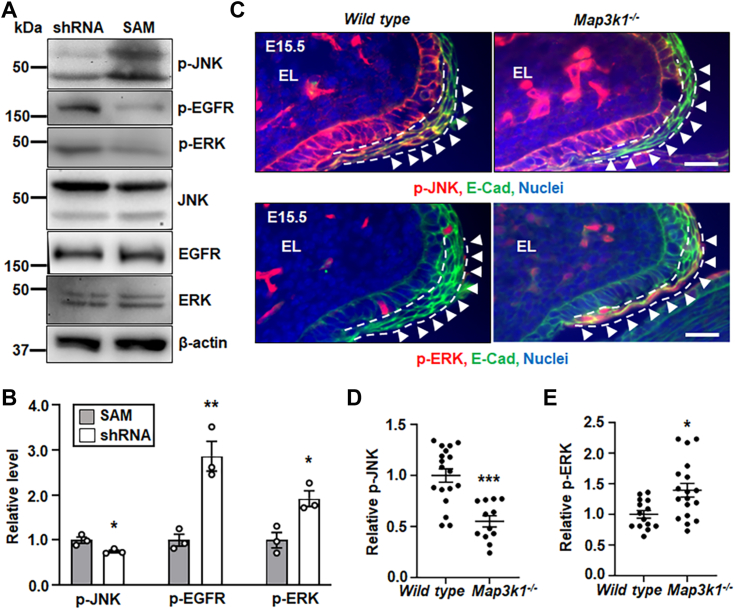
Figure 4.
The MAP3K1-JNK and EGFR-ERK pathways inhibit each other. Lysates of the shRNA HaCaT and SAM HaCaT cells were examined by Western blotting for (A) p-JNK, p-EGFR, p-ERK, and β-actin, and (B) quantification of p-JNK, p-EGFR, and p-ERK using β-actin as a loading control. Levels in SAM HaCaT were set as 1. Data represented three independent experiments (N = 3) and were shown as mean ± SEM. C, immunofluorescence staining of WT and Map3k1−/− E15.5 embryonic eyelids with anti-p-JNK (red, top panels) and anti-p-ERK (red, bottom panels), costained with anti-E-cadherin (green) that marks epithelial membrane, and Hoechst (blue) labels nuclei. Representative images were shown, the scale bars represent 50 μm. The (D) p-JNK, and (E) p-ERK, in the suprabasal epithelial cells, marked with dash lines, of the eyelid leading edge (arrowheads) were quantified and compared to that in WT, set as 1. At least three sections (N ≥ 3) per embryo and three embryos (N ≥ 3) of each genotype from different litters were examined. Data were shown as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 were considered significantly different from SAM cells (in B) and WT embryos (in D and E). EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; MAP3K1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1; SAM, synergistic activation mediator.