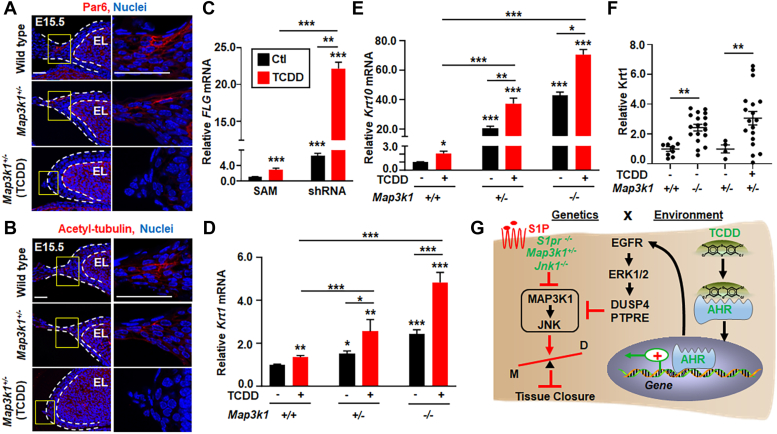
Figure 7.
TCDD and Map3k1 loss-of-function disrupt cell polarity and potentiate epithelial terminal differentiation. Eyelids of E15.5 WT, Map3k1+/−, and TCDD treated Map3k1+/− embryos were subjected to immunohistochemistry using (A) anti-Par6 and (B) anti-acetylated-tubulin, detecting apical epithelial polarity and Hoechst labeling nuclei. Dash lines mark the eyelid epithelium. The scale bar represents 50 μm. C, the expression of Filaggrin (FLG), a marker of terminally differentiated keratinocytesin the granular and cornified epidermis, examined by qRT-PCR in shRNA HaCaT and SAM HaCaT treated with 10 nM TCDD or vehicle (DMSO, Ctl). The relative FLG mRNA was calculated using the housekeeping gene GAPDH as an internal control. FLG levels in SAM (Ctl) were set as 1, expression of (D) Krt1 and (E) Krt10, markers of the differentiating suprabasal keratinocytes, were examined in WT, Map3k1+/−, and Map3k1−/− keratinocytes treated with 10 nM TCDD or vehicle (DMSO). Relative expression was calculated using the housekeeping gene GAPDH as an internal control and compared to levels in WT keratinocytes set as 1. F, the E15.5 embryos of WT, Map3k1−/−, and Map3k1+/− with or without TCDD exposure were examined by immunohistochemistry for Krt1. Staining signals were quantified, and relative expression was calculated. Data are mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments (N ≥ 3) or at least three eye sections (N ≥ 3) per embryo and three embryos (N ≥ 3) from different litters. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 were considered statistically significant compared to WT and SAM untreated or as indicated. G, graphic illustration of the proposed GxE interactions model in eyelid closure defects. The environmental factor TCDD activates the AHR to induce gene expression and activate the EGFR-ERK pathways. EGFR signaling in turn induces phosphatases to inhibit the S1PR-MAP3K1-JNK pathway. This effect of TCDD is trivial and insufficient to induce the eyelid phenotype. However, in the presence of gene mutations, i.e., S1pr2/3−/−, Map3k1+/− and Jnk1−/−, which also slightly attenuate MAP3K1-JNK signaling, the effect of TCDD is largely amplified. As the results, the GxE interactions significantly inhibit JNK, accelerate differentiation (D) and impede morphogenesis (M) of the epithelium, leading to defective tissue closure. AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; Krt1, keratin 1; MAP3K1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription PCR; S1P, sphigosin-1-phosphate; SAM, synergistic activation mediator; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin.